Significance of the Wnt signaling pathway in coronary artery atherosclerosis
- PMID: 38586172
- PMCID: PMC10995361
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1360380
Significance of the Wnt signaling pathway in coronary artery atherosclerosis
Abstract
Introduction: The progression of coronary atherosclerosis is an active and regulated process. The Wnt signaling pathway is thought to play an active role in the pathogenesis of several cardiovascular diseases; however, a better understanding of this system in atherosclerosis is yet to be unraveled.
Methods: In this study, real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blotting were used to quantify the expression of Wnt3a, Wnt5a, and Wnt5b in the human coronary plaque, and immunohistochemistry was used to identify sites of local expression. To determine the pathologic significance of increased Wnt, human vascular smooth muscle cells (vSMCs) were treated with Wnt3a, Wnt5a, and Wnt5b recombinant proteins and assessed for changes in cell differentiation and function.
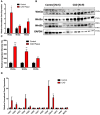
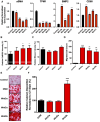
Results: RT-PCR and Western blotting showed a significant increase in the expression of Wnt3a, Wnt5a, Wnt5b, and their receptors in diseased coronary arteries compared with that in non-diseased coronary arteries. Immunohistochemistry revealed an abundant expression of Wnt3a and Wnt5b in diseased coronary arteries, which contrasted with little or no signals in normal coronary arteries. Immunostaining of Wnt3a and Wnt5b was found largely in inflammatory cells and myointimal cells. The treatment of vSMCs with Wnt3a, Wnt5a, and Wnt5b resulted in increased vSMC differentiation, migration, calcification, oxidative stress, and impaired cholesterol handling.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the upregulation of three important members of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways and their receptors in coronary atherosclerosis and shows an important role for these molecules in plaque development through increased cellular remodeling and impaired cholesterol handling.
Keywords: RT-PCR; cholesterol efflux; human; immunohistochemistry; vascular smooth muscle cells.
© 2024 Khan, Yu, Tardif, Rhéaume, Al-Kindi, Filimon, Pop, Genest, Cecere and Schwertani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers at the time of submission. However, this had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Wnt5a attenuates Wnt3a-induced alkaline phosphatase expression in dental follicle cells.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Aug 1;336(1):85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.06.013. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 26112214
-
MiRNA-21a, miRNA-145, and miRNA-221 Expression and Their Correlations with WNT Proteins in Patients with Obstructive and Non-Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 18;24(24):17613. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417613. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139440 Free PMC article.
-
Redundant expression of canonical Wnt ligands in human breast cancer cell lines.Oncol Rep. 2006 Mar;15(3):701-7. Oncol Rep. 2006. PMID: 16465433
-
WNT5B in Physiology and Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 4;9:667581. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.667581. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34017835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt5a: a player in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and other inflammatory disorders.Atherosclerosis. 2014 Nov;237(1):155-62. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.08.027. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Atherosclerosis. 2014. PMID: 25240110 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Cells to Plaques: The Molecular Pathways of Coronary Artery Calcification and Disease.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 23;13(21):6352. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216352. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Sclerostin in Cardiovascular System.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 9;26(10):4552. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104552. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considerations on the Development of Therapeutics in Vascular Calcification.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 May 29;12(6):206. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12060206. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40558641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased Serum Sclerostin Level Is a Risk Factor for Peripheral Artery Disease in Patients with Hypertension.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jul 1;61(7):1204. doi: 10.3390/medicina61071204. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40731833 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms linking atherosclerosis to ischemic stroke: insights from DNA methylation and transcriptome integration.Front Genet. 2025 Jun 18;16:1567951. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1567951. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40606664 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

