Effects of aerobic exercise on children's executive function and academic performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38586404
- PMCID: PMC10998207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28633
Effects of aerobic exercise on children's executive function and academic performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of exercise on executive function in children, providing an evidence-based foundation to inform future research in school physical education and health education.
Methods: We searched ten databases: Cochrane Library, Scopus, OVID, Web of Science, PubMed, EBSCOhost, SPORTDiscus, PsycINFO, CNKI, WANFANG DATA, VIP, and SinoMed, and eight articles were included. Applying the revised Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool for Randomized Trials (RoB2), funnel plots and Egger regression analysis were integrated with R meta-analysis to screen for publication bias. The quality of the evidence was appraised using the Grading system.
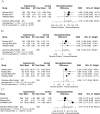
Results: The included literature contained 2655 participants, with 1308 in the experimental group and 1347 in the control group. The results indicated that the aerobic exercise group considerably improved inhibitory control in children compared to the control group [SMD = 0.29, 95% CI (0.05, 0.54), P = 0.018]; working memory [SMD = 0.25, 95% CI (0.07, 0.42), P = 0.005]; and cognitive flexibility [SMD = 0.36, 95% CI (0.17, 0.54), P < 0.001]. However, the findings indicated that only aerobic exercise interventions extending beyond 50 weeks positively influenced academic performance in children [SMD = 1.19, 95% CI (0.34, 2.04), P = 0.006]. The results of an Egger regression analysis revealed that the p-values for inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and academic performance were more significant than 0.1. The Grade system said that the quality of evidence was all low regarding the level of evidence.
Conclusion: Aerobic exercise enhanced executive function but only aerobic exercise interventions extending beyond 50 weeks demonstrated a significant effect on the academic performance of children. Due to the low quality of evidence presented in this study, additional high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: Academic performance; Aerobic exercise; Children; Executive function; Meta-analysis.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of exercise intervention on executive function in children with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PeerJ. 2025 Apr 14;13:e19273. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19273. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40247830 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of aerobic exercise on executive function among overweight and obese children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 28;15:1485610. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1485610. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39529725 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of aerobic exercise on the improvement of executive function in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychol. 2024 Jun 4;15:1376354. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1376354. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38952825 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Acute and Chronic Exercises on Executive Function in Children and Adolescents: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Psychol. 2020 Dec 17;11:554915. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.554915. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 33391074 Free PMC article.
-
School-based interventions for reducing disciplinary school exclusion: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 9;14(1):i-216. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.1. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131379 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of exercise intervention on executive function in children with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PeerJ. 2025 Apr 14;13:e19273. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19273. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40247830 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of aerobic exercise on executive function in children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Aug 30;17(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s13102-025-01304-1. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40885970 Free PMC article.
-
A longitudinal study on the effect of aerobic exercise intervention on the inhibitory control in college students with internet addiction.Front Hum Neurosci. 2025 Feb 26;19:1500399. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1500399. eCollection 2025. Front Hum Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40078486 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of the Interactive Floor Device and Aerobic Training on Executive Functions in Children.Children (Basel). 2024 Dec 6;11(12):1489. doi: 10.3390/children11121489. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zelazo P.D., Carlson S.M. Hot and cool executive function in childhood and adolescence: development and plasticity. Child Devel. Perspectiv. 2012;6:354–360.
-
- Babic M.J., Morgan P.J., Plotnikoff R.C., Lonsdale C., White R.L., Lubans D.R. Physical activity and physical self-concept in youth: systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2014;44:1589–1601. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2007. Paediatric Exercise Physiology.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

