Identifying human pre-mRNA cleavage and polyadenylation factors by genome-wide CRISPR screens using a dual fluorescence readthrough reporter
- PMID: 38587191
- PMCID: PMC11077057
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae240
Identifying human pre-mRNA cleavage and polyadenylation factors by genome-wide CRISPR screens using a dual fluorescence readthrough reporter
Abstract
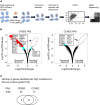
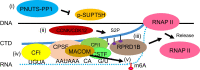
Messenger RNA precursors (pre-mRNA) generally undergo 3' end processing by cleavage and polyadenylation (CPA), which is specified by a polyadenylation site (PAS) and adjacent RNA sequences and regulated by a large variety of core and auxiliary CPA factors. To date, most of the human CPA factors have been discovered through biochemical and proteomic studies. However, genetic identification of the human CPA factors has been hampered by the lack of a reliable genome-wide screening method. We describe here a dual fluorescence readthrough reporter system with a PAS inserted between two fluorescent reporters. This system enables measurement of the efficiency of 3' end processing in living cells. Using this system in combination with a human genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 library, we conducted a screen for CPA factors. The screens identified most components of the known core CPA complexes and other known CPA factors. The screens also identified CCNK/CDK12 as a potential core CPA factor, and RPRD1B as a CPA factor that binds RNA and regulates the release of RNA polymerase II at the 3' ends of genes. Thus, this dual fluorescence reporter coupled with CRISPR/Cas9 screens reliably identifies bona fide CPA factors and provides a platform for investigating the requirements for CPA in various contexts.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




Similar articles
-
3' end formation of pre-mRNA and phosphorylation of Ser2 on the RNA polymerase II CTD are reciprocally coupled in human cells.Genes Dev. 2014 Feb 15;28(4):342-56. doi: 10.1101/gad.231274.113. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24478330 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated pre-mRNA 3' end processing activity in cancer cells renders vulnerability to inhibition of cleavage and polyadenylation.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 1;14(1):4480. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39793-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37528120 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of CFIm25 knockout on RNA polymerase II transcription.BMC Res Notes. 2018 Dec 14;11(1):894. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-4006-1. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 30547832 Free PMC article.
-
Recent molecular insights into canonical pre-mRNA 3'-end processing.Transcription. 2020 Apr;11(2):83-96. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2020.1777047. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Transcription. 2020. PMID: 32522085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyadenylation: a tail of two complexes.Curr Biol. 2002 Dec 23;12(24):R855-7. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01353-2. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12498707 Review.
Cited by
-
RPRD1B's direct interaction with phosphorylated RNA polymerase II regulates polyadenylation of cell cycle genes and drives cancer progression.RSC Chem Biol. 2025 Jan 22;6(3):423-437. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00212a. eCollection 2025 Mar 5. RSC Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 39886382 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of CDK12 in oocyte leads to female infertility.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Mar 27;16(1):213. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07536-w. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40148269 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated TGF-β1 impairs synaptic and cognitive function through activation of Smad2/3-Sp1 pathway in AngII-related hypertension.EMBO Rep. 2025 Jun;26(12):3162-3186. doi: 10.1038/s44319-025-00470-0. Epub 2025 May 27. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 40425782 Free PMC article.
-
The CDK9-SPT5 Axis in Control of Transcription Elongation by RNAPII.J Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 1;437(1):168746. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168746. Epub 2024 Aug 13. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39147127 Review.
-
CREPT is required for the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer through a co-operational-chromatin loop-based gene regulation.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jun 10;24(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02361-3. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40495214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colgan D.F., Manley J.L.. Mechanism and regulation of mRNA polyadenylation. Genes Dev. 1997; 11:2755–2766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

