Associations of Intrapancreatic Fat Deposition With Incident Diseases of the Exocrine and Endocrine Pancreas: A UK Biobank Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 38587286
- PMCID: PMC11142652
- DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002792
Associations of Intrapancreatic Fat Deposition With Incident Diseases of the Exocrine and Endocrine Pancreas: A UK Biobank Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Introduction: To investigate whether increased intrapancreatic fat deposition (IPFD) heightens the risk of diseases of the exocrine and endocrine pancreas.
Methods: A prospective cohort study was conducted using data from the UK Biobank. IPFD was quantified using MRI and a deep learning-based framework called nnUNet. The prevalence of fatty change of the pancreas (FP) was determined using sex- and age-specific thresholds. Associations between IPFD and pancreatic diseases were assessed with multivariate Cox-proportional hazard model adjusted for age, sex, ethnicity, body mass index, smoking and drinking status, central obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, liver fat content, and spleen fat content.
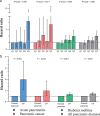
Results: Of the 42,599 participants included in the analysis, the prevalence of FP was 17.86%. Elevated IPFD levels were associated with an increased risk of acute pancreatitis (hazard ratio [HR] per 1 quintile change 1.513, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.179-1.941), pancreatic cancer (HR per 1 quintile change 1.365, 95% CI 1.058-1.762) and diabetes mellitus (HR per 1 quintile change 1.221, 95% CI 1.132-1.318). FP was also associated with a higher risk of acute pancreatitis (HR 3.982, 95% CI 2.192-7.234), pancreatic cancer (HR 1.976, 95% CI 1.054-3.704), and diabetes mellitus (HR 1.337, 95% CI 1.122-1.593, P = 0.001).
Discussion: FP is a common pancreatic disorder. Fat in the pancreas is an independent risk factor for diseases of both the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Petrov MS, Taylor R. Intra-pancreatic fat deposition: Bringing hidden fat to the fore. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;19(3):153–68. - PubMed
-
- Molnar L, Kerekes E, Meszaros A. Significance of the fatty infiltration of the pancreas [in Hungarian]. Orv Hetil 1958;99(36):1243–6. - PubMed
-
- Petrov MS. Fatty change of the pancreas: The Pandora's box of pancreatology. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023;8(7):671–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82200680/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82200720/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82200721/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82070996/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82241043/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173616/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- YZ2021147/Natural ScienCultivation Foundation of Yangzhou Municipal Key Laboratoryce Foundation of Yangzhou Municipality
- ZD2022011/The Medical research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- YZ2022080/Yangzhou key research and development plan
- SZS2023001/Suzhou Innovation Platform Construction Projects- Municipal Key Laboratory Construction
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

