Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy: More Than Meets the Eye
- PMID: 38587287
- PMCID: PMC11365597
- DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002795
Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy: More Than Meets the Eye
Abstract
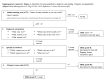
Introduction: We aimed to assess the reliability of a qualitative approach to overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) diagnosis compared with the semiquantitative, and recommended one.
Methods: The above 2 methods were compared in 411 outpatients (71% males, 60 ± 10 years, model for end-stage liver disease 13.5 ± 5.0).
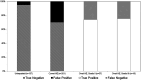
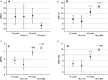
Results: Of the 73 patients with OHE on quantitative assessment, 19 (26%) were missed on qualitative assessment, with no difference in the likelihood of the physician missing grades II or III. Sixty-eight (20%) of the 270 patients with no OHE on quantitative assessment were wrongly qualified as having OHE.
Discussion: Qualitative clinical evaluation of OHE is not reliable, and recommendations should be followed.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, et al. . Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014;60(2):715–35. - PubMed
-
- Montagnese S, Russo FP, Amodio P, et al. . Hepatic encephalopathy 2018: A clinical practice guideline by the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF). Dig Liver Dis 2019;51(2):190–205. - PubMed
-
- Rehnström S, Simert G, Hansson JA, et al. . Chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A psychometrical study. Scand J Gastroenterol 1977;12(3):305–11. - PubMed
-
- Amodio P, Montagnese S, Gatta A, et al. . Characteristics of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2004;19(3-4):253–67. - PubMed
-
- Mangini C, Zarantonello L, Formentin C, et al. . Evolution of hepatic encephalopathy over time: Ecological data from a tertiary referral centre for hepatology. Dig Liver Dis 2023;55(1):93–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

