Estrogenic, androgenic, and genotoxic activities of zearalenone and deoxynivalenol in in vitro bioassays including exogenous metabolic activation
- PMID: 38587710
- PMCID: PMC11258189
- DOI: 10.1007/s12550-024-00529-2
Estrogenic, androgenic, and genotoxic activities of zearalenone and deoxynivalenol in in vitro bioassays including exogenous metabolic activation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Estrogenic, androgenic, and genotoxic activities of zearalenone and deoxynivalenol in in vitro bioassays including exogenous metabolic activation.Mycotoxin Res. 2024 Aug;40(3):347-349. doi: 10.1007/s12550-024-00535-4. Mycotoxin Res. 2024. PMID: 38668791 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
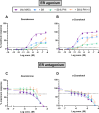
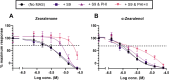
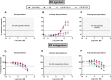
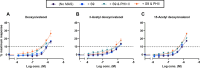
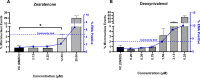
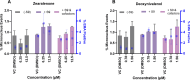
Zearalenone (ZEN) and deoxynivalenol (DON) and their derivatives are well-known mycotoxins, which can occur not only in crops but also in water bodies, including drinking water sources. In vitro bioassays can be used to detect biological effects of hazardous compounds in water. To this, when studying biological effects and toxicity in vitro, metabolism is important to consider. In this study, ZEN, α-zearalenol (α-ZEL), DON, 3-acetyl DON, and 15-acetyl DON were evaluated in vitro for hormone receptor-mediated effects (estrogen receptor [ER] and androgen receptor [AR]) and genotoxicity (micronucleus assay) in the presence of an exogenous metabolic activation system (MAS). The ER bioassay proved to be a highly sensitive method to detect low concentrations of the ZEN compounds (EC10 values of 31.4 pM for ZEN, 3.59 pM for α-ZEL) in aqueous solutions. In the presence of the MAS, reduced estrogenic effects were observed for both ZEN compounds (EC10 values of 6.47 × 103 pM for ZEN, 1.55 × 102 pM for α-ZEL). Of the DON compounds, only 3-acetyl DON was estrogenic (EC10 of 0.31 µM), and the effect was removed in the presence of the MAS. Anti-androgenic effects of the ZEN compounds and androgenic effects of the DON compounds were detected in the micromolar range. No induction of genotoxicity was detected for ZEN or DON in the presence of the MAS. Our study highlighted that inclusion of exogenous MAS is a useful tool to detect biological effects of metabolites in in vitro bioassays.
Keywords: In vitro bioassays; Deoxynivalenol; Effect-based methods; Endocrine receptors; Metabolism; Micronuclei formation; Zearalenone.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered potential competing interests. J.L. and A.O. are co-founders and owners of BioCell Analytica Uppsala AB, a company providing effect-based testing services to the water sector.
Figures
References
-
- Abid-Essefi S, Baudrimont I, Hassen W, Ouanes Z, Mobio TA, Anane R, Creppy EE, Bacha H. DNA fragmentation, apoptosis and cell cycle arrest induced by zearalenone in cultured DOK, Vero and Caco-2 cells: prevention by vitamin E. Toxicology. 2003;192(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/S0300-483X(03)00329-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Gabr HM, Zheng T, Yu X. Fungi contamination of drinking water BT - reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. In: Whitacre DM, editor. Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer International Publishing; 2014. pp. 121–139. - PubMed
-
- Beltman W, de Vries I, Meulenbelt J (2000) Rijksinstituut Voor Volksgezondheid En Milieu National Institute of Public Health and the Environment. In Rivm.Nl (Issue April). http://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/257852004.pdf
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

