Geographical and climatic distribution of lentil-nodulating rhizobia in Iran
- PMID: 38587812
- PMCID: PMC11044965
- DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiae046
Geographical and climatic distribution of lentil-nodulating rhizobia in Iran
Abstract
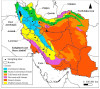
Lentil is one of the most important legumes cultivated in various provinces of Iran. However, there is limited information about the symbiotic rhizobia of lentils in this country. In this study, molecular identification of lentil-nodulating rhizobia was performed based on 16S-23S rRNA intergenic spacer (IGS) and recA, atpD, glnII, and nodC gene sequencing. Using PCR-RFLP analysis of 16S-23S rRNA IGS, a total of 116 rhizobia isolates were classified into 20 groups, leaving seven strains unclustered. Phylogenetic analysis of representative isolates revealed that the rhizobia strains belonged to Rhizobium leguminosarum and Rhizobium laguerreae, and the distribution of the species is partially related to geographical location. Rhizobium leguminosarum was the dominant species in North Khorasan and Zanjan, while R. laguerreae prevailed in Ardabil and East Azerbaijan. The distribution of the species was also influenced by agroecological climates; R. leguminosarum thrived in cold semiarid climates, whereas R. laguerreae adapted to humid continental climates. Both species exhibited equal dominance in the Mediterranean climate, characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters, in Lorestan and Kohgiluyeh-Boyer Ahmad provinces.
Keywords: Lens culinaris; Rhizobium; multilocus sequence analysis; phylogeny; symbiotic genes.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abadi VAJM, Sepehri M, Khatabi B et al. Alleviation of zinc deficiency in wheat inoculated with root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica and rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida. Rhizosphere. 2021;17:100311.
-
- Abadi VAJM, Sepehri M, Rahmani HA et al. Role of dominant phyllosphere bacteria with plant growth–promoting characteristics on growth and nutrition of maize (Zea mays L.). J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2020;20:2348–63.
-
- Abraham R. Lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) current status and future prospect of production in Ethiopia. Adv Plants Agric Res. 2015;2:00040.
-
- Adesemoye A, Torbert H, Kloepper J. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria allow reduced application rates of chemical fertilizers. Microb Ecol. 2009;58:921–9. - PubMed

