The Pan-RAF-MEK Nondegrading Molecular Glue NST-628 Is a Potent and Brain-Penetrant Inhibitor of the RAS-MAPK Pathway with Activity across Diverse RAS- and RAF-Driven Cancers
- PMID: 38588399
- PMCID: PMC11215411
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0139
The Pan-RAF-MEK Nondegrading Molecular Glue NST-628 Is a Potent and Brain-Penetrant Inhibitor of the RAS-MAPK Pathway with Activity across Diverse RAS- and RAF-Driven Cancers
Abstract
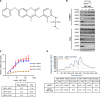
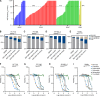
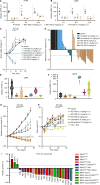
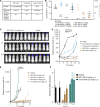
Alterations in the RAS-MAPK signaling cascade are common across multiple solid tumor types and are a driver for many cancers. NST-628 is a potent pan-RAF-MEK molecular glue that prevents the phosphorylation and activation of MEK by RAF, overcoming the limitations of traditional RAS-MAPK inhibitors and leading to deep durable inhibition of the pathway. Cellular, biochemical, and structural analyses of RAF-MEK complexes show that NST-628 engages all isoforms of RAF and prevents the formation of BRAF-CRAF heterodimers, a differentiated mechanism from all current RAF inhibitors. With a potent and durable inhibition of the RAF-MEK signaling complex as well as high intrinsic permeability into the brain, NST-628 demonstrates broad efficacy in cellular and patient-derived tumor models harboring diverse MAPK pathway alterations, including orthotopic intracranial models. Given its functional and pharmacokinetic mechanisms that are differentiated from previous therapies, NST-628 is positioned to make an impact clinically in areas of unmet patient need. Significance: This study introduces NST-628, a molecular glue having differentiated mechanism and drug-like properties. NST-628 treatment leads to broad efficacy with high tolerability and central nervous system activity across multiple RAS- and RAF-driven tumor models. NST-628 has the potential to provide transformative clinical benefits as both monotherapy and vertical combination anchor.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
M.B. Ryan reports other support from Nested Therapeutics during the conduct of the study. B. Quade reports other support from Nested Therapeutics, Inc. during the conduct of the study. S.E. Cohen reports that he is an employee of and shareholder in Nested Therapeutics. A. Ozen reports being an employee with equity interest in Nested Therapeutics. C. Ye reports other support from Nested Therapeutics during the conduct of the study. A.C. Dar reports personal fees and other support from Nested Therapeutics during the conduct of the study; and ACD is a cofounder, consultant, shareholder, and advisory board member to Nested Therapeutics. K.P. Hoeflich reports personal fees from Turbine AI outside the submitted work. M. Hale reports a patent for WO/2023/211812 pending. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures



References
-
- Ryan MB, Corcoran RB. Therapeutic strategies to target RAS-mutant cancers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018;15:709–20. - PubMed
-
- Papke B, Der CJ. Drugging RAS: know the enemy. Science 2017;355:1158–63. - PubMed
-
- Kun E, Tsang YTM, Ng CW, Gershenson DM, Wong KK. MEK inhibitor resistance mechanisms and recent developments in combination trials. Cancer Treat Rev 2021;92:102137. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y, Adjei AA. The clinical development of MEK inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2014;11:385–400. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

