Development and validation of an individualised nomogram to predict mother-to-child transmission in pregnant women with syphilis in China: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38589256
- PMCID: PMC11015325
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080211
Development and validation of an individualised nomogram to predict mother-to-child transmission in pregnant women with syphilis in China: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Objectives: The elimination of mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of syphilis has been set as a public health priority. However, an instrument to predict the MTCT of syphilis is not available. We aimed to develop and validate an intuitive nomogram to predict the individualised risk of MTCT in pregnant women with syphilis in China.
Design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Data was acquired from the National Information System of Prevention of MTCT of Syphilis in Guangdong province between 2011 and 2020.
Participants: A total of 13 860 pregnant women with syphilis and their infants were included and randomised 7:3 into the derivation cohort (n=9702) and validation cohort (n=4158).
Primary outcome measures: Congenital syphilis.
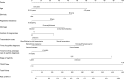
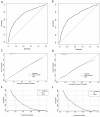
Results: Among 13 860 pregnant women with syphilis and their infants included, 1370 infants were diagnosed with congenital syphilis. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression and multivariable logistic regression showed that age, ethnicity, registered residence, marital status, number of pregnancies, transmission route, the timing of syphilis diagnosis, stage of syphilis, time from first antenatal care to syphilis diagnosis and toluidine red unheated serum test titre were predictors of MTCT of syphilis. A nomogram was developed based on the predictors, which demonstrated good calibration and discrimination with an area under the curve of the receiver operating characteristic of 0.741 (95% CI: 0.728 to 0.755) and 0.731 (95% CI: 0.710 to 0.752) for the derivation and validation cohorts, respectively. The net benefit of the predictive models was positive, demonstrating a significant potential for clinical decision-making. We have also developed a web calculator based on this prediction model.
Conclusions: Our nomogram exhibited good performance in predicting individualised risk for MTCT of syphilis, which may help guide early and personalised prevention for MTCT of syphilis.
Keywords: epidemiology; public health; risk factors; syphilis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strategies of testing for syphilis during pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Oct 29;2014(10):CD010385. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010385.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25352226 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Syphilis in pregnant women and congenital syphilis from 2012 to 2021 in Switzerland: a multicentre, retrospective study.Swiss Med Wkly. 2024 Nov 1;154:3678. doi: 10.57187/s.3678. Swiss Med Wkly. 2024. PMID: 39509430
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
References
-
- Gao S, Zhu Y-X, Liang H-Y, et al. . Effect of elimination on HIV, Syphilis AND hepatitis B transmission by mother to child in Guangdong province, 2016—2020. Chin J Health Edu 2021;37:872-75+93. 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2021.10.002 - DOI
-
- Qin J-B, Feng T-J, Yang T-B, et al. . Synthesized prevention and control of one decade for mother-to-child transmission of Syphilis and determinants associated with congenital Syphilis and adverse pregnancy outcomes in Shenzhen, South China. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2014;33:2183–98. 10.1007/s10096-014-2186-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
