The agreement between bronchoalveolar lavage, bronchial wash and sputum culture: a retrospective study
- PMID: 38589747
- PMCID: PMC11289070
- DOI: 10.1007/s15010-024-02238-5
The agreement between bronchoalveolar lavage, bronchial wash and sputum culture: a retrospective study
Abstract
Purpose: Bronchoalveolar lavage is commonly used in clinical practice for unresolved pneumonia. However, bronchoalveolar lavage is not suitable for all patients as it is an invasive procedure and can worsen oxygenation. The diagnostic value of bronchial wash and sputum has been debated extensively over the years. In this study, we aim to compare the diagnostic value in several pathogens of bronchoalveolar lavage and bronchial wash, and secondarily bronchoalveolar lavage and sputum.
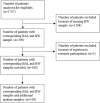
Methods: We retrospectively included all adult patients in our hospital who underwent bronchoalveolar lavage, bronchial wash, and where sputum sampling was done between January 1st of 2018 and December 31st of 2021. The intraclass correlation coefficient was computed for the three tests.
Results: In total, 308 patients were included. We found a level of correlation of 0.819 and 0.865, respectively, between bronchoalveolar lavage and bronchial wash for two pathogens: Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. For Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Aspergillus fumigatus, we found an intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.568 and 0.624, respectively. Between bronchoalveolar lavage and sputum, we found varying levels of agreement.
Conclusion: Our study shows reasonably well agreement levels between bronchoalveolar lavage and bronchial wash, suggesting that bronchial wash could potentially be an alternative to bronchoalveolar lavage.
Keywords: Bronchial wash; Bronchoalveolar lavage; Pneumonia; Sputum.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
AEP: No conflicts of interest. EB: No conflicts of interest. DFP: No conflicts of interest. DJS: No conflicts of interest. OWA: No conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Fact sheet: Top 10 causes of death. WHO. 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death. Cited 2023 January 14. Accessed 15 Jan 2024
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources