Successful treatment of severe splenic lymphoma‑associated hemophagocytic syndrome by splenectomy and subsequent chemotherapy: A case report
- PMID: 38590310
- PMCID: PMC10999785
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2024.14355
Successful treatment of severe splenic lymphoma‑associated hemophagocytic syndrome by splenectomy and subsequent chemotherapy: A case report
Abstract
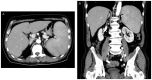
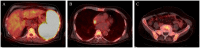
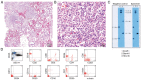
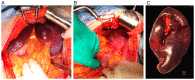
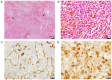
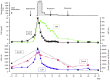
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) represents a fatal immunopathology derived from excessive inflammatory reactions. In particular, lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome (LAHS) is associated with a dismal prognosis. The current study presented a challenging case of splenic LAHS. A 71-year-old man presented with fatigue and anorexia. Laboratory test results revealed anemia, thrombocytopenia, lactate dehydrogenase elevation and markedly elevated levels of ferritin (6,210 ng/ml) and soluble interleukin 2 receptor (sIL-2R; 11,328 U/ml). Abdominal computed tomography revealed marked splenomegaly, while fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography revealed increased tracer uptake in the spleen. An elective splenectomy was performed, which led to the diagnosis of B-cell splenic lymphoma with transformation from indolent to aggressive lymphoma. Prior to the splenectomy, thrombocytopenia and hepatic dysfunction with rapidly progressing jaundice appeared, accompanying further elevation of ferritin (25,197 ng/ml) and sIL-2R levels (30,420 U/ml). On postoperative day 5, the patient was transferred to a tertiary care institution and corticosteroid pulse therapy was immediately initiated after establishing the diagnosis of LAHS. Liver dysfunction gradually recovered and subsequent chemotherapy resulted in complete remission with improved performance status. At eight months after the onset, the patient remains alive without any signs of residual lymphoma. Although splenic lymphoma typically manifests with low-grade lymphoma, it can transform into high-grade lymphoma associated with severe complications, such as HLH and multiple organ failure. In this case, splenectomy assisted in not only establishing the diagnosis but also in tumor cytoreduction before commencing chemotherapy. Through interdisciplinary collaboration, the patient was successfully treated by performing a timely splenectomy, followed by steroid pulse therapy and chemotherapy.
Keywords: hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; hemophagocytic syndrome; lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome; splenectomy; splenomegaly.
Copyright: © 2024 Masui et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A high sIL-2R/ferritin ratio is a useful marker for the diagnosis of lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome.Ann Hematol. 2014 May;93(5):821-6. doi: 10.1007/s00277-013-1925-8. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Ann Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24705932 Free PMC article.
-
High concentration of miR-133 is a useful marker for the diagnosis of lymphoma- associated hemophagocytic syndrome.Cancer Biomark. 2017 Aug 23;20(2):159-164. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170054. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 28869447
-
Identification of clinical features of lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome (LAHS): an analysis of 69 patients with hemophagocytic syndrome from a single-center in central region of China.Med Oncol. 2014 Apr;31(4):902. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0902-y. Epub 2014 Mar 8. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24610542
-
Acquired hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis as initial manifestation of multiple myeloma: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 25;99(39):e22299. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022299. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32991435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rituximab, etoposide, methylprednisolone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin in the treatment of secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with classical Hodgkin lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2016 Dec 20;10(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-1143-9. J Med Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27998299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li F, Li P, Zhang R, Yang G, Ji D, Huang X, Xu Q, Wei Y, Rao J, Huang R, Chen G. Identification of clinical features of lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome (LAHS): An analysis of 69 patients with hemophagocytic syndrome from a single-center in central region of China. Med Oncol. 2014;31:902. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0902-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
