Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis-2 Mimicking Non-accidental Injury
- PMID: 38590732
- PMCID: PMC11000754
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001312
Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis-2 Mimicking Non-accidental Injury
Abstract
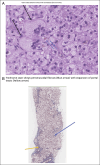
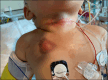
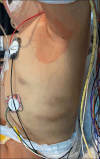
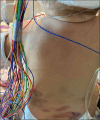
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by defective secretion of bile acids or transport defects resulting in progressive cholestasis. These disorders usually present during infancy or childhood and are associated with progressive liver disease. PFIC is estimated to affect 1 in 50,000-100,000 births, with PFIC-2 representing half of PFIC cases. PFIC-2 presents with hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, pruritus, fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies, and growth failure. Laboratory findings include low/normal gamma glutamyl transpeptidase levels and elevated bilirubin, transaminases, and alpha-fetoprotein levels. In this report, we present a case of PFIC-2 presenting with severe coagulopathy, bruising, subcutaneous hematomas, and acute-onset anemia.
Keywords: ABCB11; Cholestatic Jaundice; PFIC2; coagulopathy; progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
References
-
- Baker A, Kerkar N, Todorova L, Kamath BM, Houwen RHJ. Systematic review of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019;43(1):20–36. - PubMed
-
- Davit-Spraul A, Fabre M, Branchereau S, et al. ATP8B1 and ABCB11 analysis in 62 children with normal gamma-glutamyl transferase progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC): Phenotypic differences between PFIC1 and PFIC2 and natural history. Hepatology. 2010;51(5):1645–55. - PubMed
-
- Al Mehaidib A, Al Shahrani A. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis in Arabs. J Hepatol. 2013;58:S555–6.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

