Challenging the status quo: a framework for mechanistic and human-relevant cardiovascular safety screening
- PMID: 38590785
- PMCID: PMC10999590
- DOI: 10.3389/ftox.2024.1352783
Challenging the status quo: a framework for mechanistic and human-relevant cardiovascular safety screening
Abstract
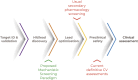
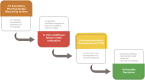
Traditional approaches to preclinical drug safety assessment have generally protected human patients from unintended adverse effects. However, these assessments typically occur too late to make changes in the formulation or in phase 1 and beyond, are highly dependent on animal studies and have the potential to lead to the termination of useful drugs due to liabilities in animals that are not applicable in patients. Collectively, these elements come at great detriment to both patients and the drug development sector. This phenomenon is particularly problematic in the area of cardiovascular safety assessment where preclinical attrition is high. We believe that a more efficient and translational approach can be defined. A multi-tiered assessment that leverages our understanding of human cardiovascular biology, applies human cell-based in vitro characterizations of cardiovascular responses to insult, and incorporates computational models of pharmacokinetic relationships would enable earlier and more translational identification of human-relevant liabilities. While this will take time to develop, the ultimate goal would be to implement such assays both in the lead selection phase as well as through regulatory phases.
Keywords: cardiac; cardiac NAM; cardiac drug development; cardiac toxicity; cardiovascular toxicity.
Copyright © 2024 Berridge, Pierson, Pettit and Stockbridge.
Conflict of interest statement
Author BB was employed by B2 Pathology Solutions, LLC. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abram S., Arruda-Olson A. M., Scott C. G., Pellikka P. A., Nkomo V. T., Oh J. K., et al. (2015). Typical blood pressure response during dobutamine stress echocardiography of patients without known cardiovascular disease who have normal stress echocardiograms. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc Imaging 17 (5), 557–563. 10.1093/ehjci/jev165 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avila A. M., Bebenek I., Bonzo J. A., Bourcier T., Davis Bruno K. L., Carlson D. B., et al. (2020). An FDA/CDER perspective on nonclinical testing strategies: classical toxicology approaches and new approach methodologies (NAMs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 114, 104662. 10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104662 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Banfor P. N., Preusser L. C., Campbell T. J., Marsh K. C., Polakowski J. S., Reinhart G. A., et al. (2008). Comparative effects of levosimendan, OR-1896, OR-1855, dobutamine, and milrinone on vascular resistance, indexes of cardiac function, and O2 consumption in dogs. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 294 (1), H238–H248. 10.1152/ajpheart.01181.2007 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

