Sources, effects and present perspectives of heavy metals contamination: Soil, plants and human food chain
- PMID: 38590838
- PMCID: PMC10999863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28357
Sources, effects and present perspectives of heavy metals contamination: Soil, plants and human food chain
Abstract
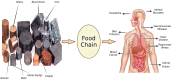
Heavy metal (HM) poisoning of agricultural soils poses a serious risk to plant life, human health, and global food supply. When HM levels in agricultural soils get to dangerous levels, it harms crop health and yield. Chromium (Cr), arsenic (As), nickel (Ni), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), zinc (Zn), and copper (Cu) are the main heavy metals. The environment contains these metals in varying degrees, such as in soil, food, water, and even the air. These substances damage plants and alter soil characteristics, which lowers crop yield. Crop types, growing circumstances, elemental toxicity, developmental stage, soil physical and chemical properties, and the presence and bioavailability of heavy metals (HMs) in the soil solution are some of the factors affecting the amount of HM toxicity in crops. By interfering with the normal structure and function of cellular components, HMs can impede various metabolic and developmental processes. Humans are exposed to numerous serious diseases by consuming these affected plant products. Exposure to certain metals can harm the kidneys, brain, intestines, lungs, liver, and other organs of the human body. This review assesses (1) contamination of heavy metals in soils through different sources, like anthropogenic and natural; (2) the effect on microorganisms and the chemical and physical properties of soil; (3) the effect on plants as well as crop production; and (4) entering the food chain and associated hazards to human health. Lastly, we identified certain research gaps and suggested further study. If people want to feel safe in their surroundings, there needs to be stringent regulation of the release of heavy metals into the environment.
Keywords: Agricultural soil; Contamination; Food chain; HMs; Heavy metals; Human health; Plants; Pollution; Toxic elements.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Uchimiya M., Bannon D., Nakanishi H., McBride M.B., Williams M.A., Yoshihara T. Chemical speciation, plant uptake, and toxicity of heavy metals in agricultural soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020;68(46):12856–12869. - PubMed
-
- Liu L., Li W., Song W., Guo M. Remediation techniques for heavy metalcontaminated soils: principles and applicability. Sci. Total Environ. 2018;633:206–219. - PubMed
-
- Mansoor S., Kour N., Manhas S., Zahid S., Wani O.A., Sharma V., Wijaya L., Alyemeni M.N., Alsahli A.A., El-Serehy H.A. Biochar as a tool for effective management of drought and heavy metal toxicity. Chemosphere. 2020;271 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

