Polyphenol-rich black currant and cornelian cherry juices ameliorate metabolic syndrome induced by a high-fat high-fructose diet in Wistar rats
- PMID: 38590904
- PMCID: PMC10999883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27709
Polyphenol-rich black currant and cornelian cherry juices ameliorate metabolic syndrome induced by a high-fat high-fructose diet in Wistar rats
Abstract
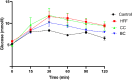
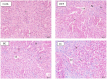
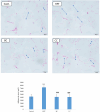
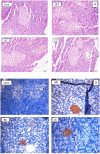
Diets high in fat and sugar lead to metabolic syndrome (MetS) and related chronic diseases. We investigated the effects of commercially available, cold-pressed polyphenol-rich black currant (BC) and cornelian cherry (CC) juices on the prevention of MetS in Wistar rats induced by a 10-weeks high-fat high-fructose (HFF) diet. Juice consumption, either BC or CC, with a HFF diet resulted in lower serum triglycerides compared to only the HFF consumption. Both juices also mitigated the effects of HFF on the liver, pancreas, and adipose tissue, by preserving liver and pancreas histomorphology and reducing visceral fat and adipocyte size. Furthermore, supplementation with both juices reduced glucagon and up-regulated insulin expression in the pancreas of the rats on the HFF diet, whereas the BC also showed improved glucose regulation. BC juice also reduced the expression of IL-6 and hepatic inflammation compared to the group only on HFF diet. Both juices, especially BC, could be a convenient solution for the prevention of MetS in humans.
Keywords: Animal model; Black currant; Cornelian cherry; High-fat high-fructose diet; Metabolic syndrome; Polyphenol-rich juices.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antioxidative Effects of Black Currant and Cornelian Cherry Juices in Different Tissues of an Experimental Model of Metabolic Syndrome in Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 24;12(6):1148. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061148. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371879 Free PMC article.
-
Grape pomace and grape pomace extract improve insulin signaling in high-fat-fructose fed rat-induced metabolic syndrome.Food Funct. 2016 Mar;7(3):1544-53. doi: 10.1039/c5fo01065a. Food Funct. 2016. PMID: 26901521
-
Black raspberry (Rubus occidentalis) attenuates inflammatory markers and vascular endothelial dysfunction in Wistar rats fed a high-fat diet with fructose solution.J Food Biochem. 2021 Oct;45(10):e13917. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13917. Epub 2021 Sep 12. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34510490
-
High Fat/High Glucose Diet Induces Metabolic Syndrome in an Experimental Rat Model.Nutrients. 2018 Oct 14;10(10):1502. doi: 10.3390/nu10101502. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30322196 Free PMC article.
-
Thirty days of combined consumption of a high-fat diet and fructose-rich beverages promotes insulin resistance and modulates inflammatory response and histomorphometry parameters of liver, pancreas, and adipose tissue in Wistar rats.Nutrition. 2021 Nov-Dec;91-92:111403. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111403. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Nutrition. 2021. PMID: 34391133
Cited by
-
Extraction, Characterization, and Nutraceutical Potential of Prosthechea karwinskii Orchid for Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress in Wistar Rats.Foods. 2024 Aug 1;13(15):2432. doi: 10.3390/foods13152432. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39123622 Free PMC article.
-
Excess Fructose Intake Activates Hyperinsulinemia and Mitogenic MAPK Pathways in Association With Cellular Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in the Pancreas of Rats.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2025 May;69(10):e70048. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.70048. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2025. PMID: 40152093 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Lipidomic Alterations in Metabolic Syndrome: A Study of Plasma, Liver, and Adipose Tissues in a Dietary-Induced Rat Model.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 13;16(20):3466. doi: 10.3390/nu16203466. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39458462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tasic N., Jakovljevic V.L.J., Mitrovic M., Djindjic B., Tasic D. Black chokeberry aronia melanocarpa extract reduces blood pressure, glycemia and lipid profile in patients with metabolic syndrome : a prospective controlled trial. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021;476:2663–2673. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04106-4. 2021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Michicotl-Meneses M.M., Thompson-Bonilla M.d.R., Reyes-López C.A., García-Pérez B.E., López-Tenorio I.I., Ordaz-Pichardo C., Jaramillo-Flores M.E. Inflammation markers in adipose tissue and cardiovascular risk reduction by pomegranate juice in obesity induced by a hypercaloric diet in wistar rats. Nutrients. 2021;13:2577. doi: 10.3390/nu13082577. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

