Effects of electroacupuncture on chronic urinary retention after pelvic or lumbosacral tumor resection surgeries: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38590962
- PMCID: PMC10999027
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-23-468
Effects of electroacupuncture on chronic urinary retention after pelvic or lumbosacral tumor resection surgeries: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Chronic urinary retention (CUR) resulting from lower motor neuron lesions (LMNL) is a medical condition secondary to pelvic or lumbosacral tumor resection surgeries. Electroacupuncture (EA) is proved to be effective and safe in treating certain lower urinary tract disorders. However, the clinical benefit and optimal duration of EA treatment for CUR following LMNL remain unknown.
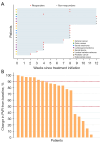
Methods: Using a retrospective cohort design, 20 eligible patients diagnosed with CUR resulting from LMNL secondary to pelvic or lumbosacral tumor resection surgeries were included from March 1, 2017, to June 30, 2020. The patients were treated by EA three times a week for 2 to 12 weeks and followed up for 24 weeks after treatment. The electric stimulators with a 5-Hz continuous wave (5-10 mA intensity) were separately connected to bilateral Ciliao (BL32), bilateral Zhongliao (BL33), and bilateral Huiyang (BL35), and stimulators with a 10-Hz continuous wave (1-2 mA intensity) were connected to bilateral Sanyinjiao (SP6). Current intensity was adjusted according to the patients' individual tolerance. The median follow-up was 32 weeks (range, 26-36 weeks). Responders were defined as patients whose post-void residuals (PVR) reduced by 50% or more from baseline. Adverse event was recorded.
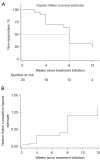
Results: Totally 20 patients [mean (standard deviation) age, 48.1 (15.5) years; 9 men (45.0%); 11 women (55.0%)] were included. Of the 20 patients, 14 (70.0%) had responded to EA treatment and stopped catheterization for achieving satisfactory spontaneous urination (PVR <100 mL without complications), 7 (35.0%) had complete resolution (90-100% reduction in PVR from baseline), and 13 (65.0%) scored 1 (much better) or 2 (moderately better) in the Patient Global Impression of Improvement (PGI-I) assessment. Moreover, 6 (30.0%) patients had responded within 4 weeks of EA treatment. According to Kaplan-Meier survival curve, we found that more than 50% patients could respond to EA treatment within 8 weeks or longer. None of the responders had ever experienced relapse in 24 weeks after EA treatment ended. None of the patients manifested urinary tract infection (UTI), newly diagnosed hydroureter or hydronephrosis. One patient diagnosed with hydronephrosis at baseline recovered after 12-week EA treatment. Two patients with UTI at baseline were prescribed antibiotics and did not present UTI again during the follow-up.
Conclusions: EA could be a promising treatment option for CUR caused by LMNL following pelvic or lumbosacral tumor resection surgeries, with long-term effects and a good safety profile. The optimal duration of EA should be of 8 weeks at least. But this was a retrospective cohort study of a small sample size, so future studies are needed to investigate EA in larger populations in randomized controlled trials.
Keywords: Chronic urinary retention (CUR); cohort study; electroacupuncture (EA); pelvic or lumbosacral tumor resection surgeries.
2024 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-23-468/coif). Y.C. is an employee of Beijing Houpu Chinese Medicine Institute Company. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of electroacupuncture on pediatric chronic urinary retention: a case-series study.Front Pediatr. 2023 Jul 21;11:1194651. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1194651. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37547105 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of electroacupuncture on patients with chronic urinary retention caused by a lower motor neuron lesion: An exploratory pilot study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(1):e18615. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018615. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 31895816 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of electroacupuncture on inflammatory signal expression in local tissues of rats with chronic pelvic pain syndrome based on purinergic 2X7 receptor/NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 signal pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2022 Dec;42(6):965-971. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220928.003. J Tradit Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 36378055 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of electroacupuncture at BL33 on detrusor smooth muscle activity in a rat model of urinary retention.Acupunct Med. 2017 Dec;35(6):437-444. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2016-011355. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Acupunct Med. 2017. PMID: 29109130 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic urinary retention in men: how we define it, and how does it affect treatment outcome.BJU Int. 2012 Dec;110(11):1590-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11101.x. Epub 2012 Mar 27. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 22452619 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term electroacupuncture for low anterior resection syndrome in postoperative rectal cancer patients: case reports.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 18;12:1517325. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1517325. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40606449 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karani R, Mahdy A, Asghar F. Postoperative Urinary Retention in Patients Who Undergo Joint Arthroplasty or Spine Surgery. JBJS Rev 2020;8:e18.00040. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
