Uncovering the burden of hidradenitis suppurativa misdiagnosis and underdiagnosis: a machine learning approach
- PMID: 38591045
- PMCID: PMC10999681
- DOI: 10.3389/fmedt.2024.1200400
Uncovering the burden of hidradenitis suppurativa misdiagnosis and underdiagnosis: a machine learning approach
Abstract
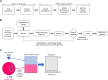
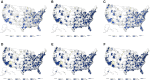
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory follicular skin condition that is associated with significant psychosocial and economic burden and a diminished quality of life and work productivity. Accurate diagnosis of HS is challenging due to its unknown etiology, which can lead to underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis that results in increased patient and healthcare system burden. We applied machine learning (ML) to a medical and pharmacy claims database using data from 2000 through 2018 to develop a novel model to better understand HS underdiagnosis on a healthcare system level. The primary results demonstrated that high-performing models for predicting HS diagnosis can be constructed using claims data, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 81%-82% observed among the top-performing models. The results of the models developed in this study could be input into the development of an impact of inaction model that determines the cost implications of HS diagnosis and treatment delay to the healthcare system.
Keywords: dermatology; diagnosis; hidradenitis suppurativa; machine learning; model; prediction.
© 2024 Kirby, Kim, Zivkovic, Wang, Garg, Danavar, Li, Chen and Garg.
Conflict of interest statement
http://cdn.elsevier.com/promis_misc/JID_COI_2013.pdf JK is a consultant for AbbVie, ChemoCentryx, Incyte, InflaRx, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, UCB, and Viela Bio and receives honorarium. JK is a speaker for AbbVie, Janssen, and UCB. KK was previously an employee of AbbVie for a portion of this study and may own AbbVie stock or stock options. MZ is an employee of Genesis Research that provided consulting services to AbbVie. SW was previously an employee of Genesis Research for a portion of this study. VG, AD, CL, and NC are employees of AbbVie and may own AbbVie stock or stock options. AG is an advisor for AbbVie, Aclaris Therapeutics, AnaptysBio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cosmo Pharmaceuticals, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, UCB, UNION Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Bio and receives honoraria. AG receives research grants from AbbVie, UCB, the National Psoriasis Foundation, and the CHORD COUSIN Collaboration (C3).
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

