Comparative efficacy of sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world experience
- PMID: 38591092
- PMCID: PMC10999032
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.463
Comparative efficacy of sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world experience
Abstract
Background: Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) are a class of drugs with modest antidiabetic efficacy, weight loss effect, and cardiovascular benefits as proven by multiple randomised controlled trials (RCTs). However, real-world data on the comparative efficacy and safety of individual SGLT-2i medications is sparse.
Aim: To study the comparative efficacy and safety of SGLT-2i using real-world clinical data.
Methods: We evaluated the comparative efficacy data of 3 SGLT-2i drugs (dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, and empagliflozin) used for treating patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Data on the reduction of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), body weight, blood pressure (BP), urine albumin creatinine ratio (ACR), and adverse effects were recorded retrospectively.
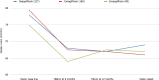
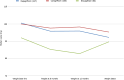
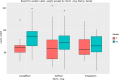
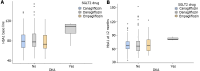
Results: Data from 467 patients with a median age of 64 (14.8) years, 294 (62.96%) males and 375 (80.5%) Caucasians were analysed. Median diabetes duration was 16.0 (9.0) years, and the duration of SGLT-2i use was 3.6 (2.1) years. SGLT-2i molecules used were dapagliflozin 10 mg (n = 227; 48.6%), canagliflozin 300 mg (n = 160; 34.3%), and empagliflozin 25 mg (n = 80; 17.1). Baseline median (interquartile range) HbA1c in mmol/mol were: dapagliflozin - 78.0 (25.3), canagliflozin - 80.0 (25.5), and empagliflozin - 75.0 (23.5) respectively. The respective median HbA1c reduction at 12 months and the latest review (just prior to the study) were: 66.5 (22.8) & 69.0 (24.0), 67.0 (16.3) & 66.0 (28.0), and 67.0 (22.5) & 66.5 (25.8) respectively (P < 0.001 for all comparisons from baseline). Significant improvements in body weight (in kilograms) from baseline to study end were noticed with dapagliflozin - 101 (29.5) to 92.2 (25.6), and canagliflozin 100 (28.3) to 95.3 (27.5) only. Significant reductions in median systolic and diastolic BP, from 144 (21) mmHg to 139 (23) mmHg; (P = 0.015), and from 82 (16) mmHg to 78 (19) mmHg; (P < 0.001) respectively were also observed. A significant reduction of microalbuminuria was observed with canagliflozin only [ACR 14.6 (42.6) at baseline to 8.9 (23.7) at the study end; P = 0.043]. Adverse effects of SGLT-2i were as follows: genital thrush and urinary infection - 20 (8.8%) & 17 (7.5%) with dapagliflozin; 9 (5.6%) & 5 (3.13%) with canagliflozin; and 4 (5%) & 4 (5%) with empagliflozin. Diabetic ketoacidosis was observed in 4 (1.8%) with dapagliflozin and 1 (0.63%) with canagliflozin.
Conclusion: Treatment of patients with SGLT-2i is associated with statistically significant reductions in HbA1c, body weight, and better than those reported in RCTs, with low side effect profiles. A review of large-scale real-world data is needed to inform better clinical practice decision making.
Keywords: Albumin creatinine ratio; Canagliflozin; Cardiovascular disease; Dapagliflozin; Diabesity; Empagliflozin; Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lower Risk of Heart Failure and Death in Patients Initiated on Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Versus Other Glucose-Lowering Drugs: The CVD-REAL Study (Comparative Effectiveness of Cardiovascular Outcomes in New Users of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors).Circulation. 2017 Jul 18;136(3):249-259. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029190. Epub 2017 May 18. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28522450 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Clinical Practice for Heart Failure Prevention and Treatment: Beyond Type 2 Diabetes. A Narrative Review.Adv Ther. 2022 Feb;39(2):845-861. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01989-z. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 34881413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Individual Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors.JAMA Intern Med. 2025 Mar 1;185(3):302-313. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.7357. JAMA Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39836397
-
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety Profile of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors as Add-On Therapy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.Cureus. 2021 Apr 3;13(4):e14268. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14268. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33954073 Free PMC article.
-
[Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors for patients with Type 2 diabetes].Ugeskr Laeger. 2016 Sep 19;178(38):V05160310. Ugeskr Laeger. 2016. PMID: 27649712 Review. Danish.
Cited by
-
Antidiabetic combination therapy and cardiovascular outcomes: An evidence-based approach.World J Diabetes. 2025 Apr 15;16(4):102390. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.102390. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40236868 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and heart disease: Current perspectives.World J Cardiol. 2024 May 26;16(5):240-259. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i5.240. World J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38817648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application value of weight-adjusted waist circumference index and cardiometabolic index in hypertensive patients with albuminuria: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2020.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2506813. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2506813. Epub 2025 May 28. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40437733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wanner C, Marx N. SGLT2 inhibitors: the future for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and other chronic diseases. Diabetologia. 2018;61:2134–2139. - PubMed
-
- Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2117–2128. - PubMed
-
- Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, Shaw W, Law G, Desai M, Matthews DR CANVAS Program Collaborative Group. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:644–657. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

