Cytotoxicity and Multi-Enzyme Inhibition of Nepenthes miranda Stem Extract on H838 Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells and RPA32, Elastase, Tyrosinase, and Hyaluronidase Proteins
- PMID: 38592804
- PMCID: PMC10974603
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13060797
Cytotoxicity and Multi-Enzyme Inhibition of Nepenthes miranda Stem Extract on H838 Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells and RPA32, Elastase, Tyrosinase, and Hyaluronidase Proteins
Abstract
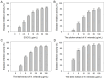
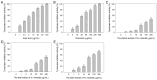
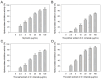
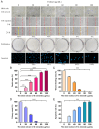
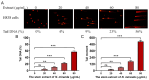
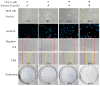
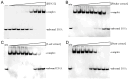
The carnivorous pitcher plants of the genus Nepenthes have long been known for their ethnobotanical applications. In this study, we prepared various extracts from the pitcher, stem, and leaf of Nepenthes miranda using 100% ethanol and assessed their inhibitory effects on key enzymes related to skin aging, including elastase, tyrosinase, and hyaluronidase. The cytotoxicity of the stem extract of N. miranda on H838 human lung carcinoma cells were also characterized by effects on cell survival, migration, proliferation, apoptosis induction, and DNA damage. The cytotoxic efficacy of the extract was enhanced when combined with the chemotherapeutic agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), indicating a synergistic effect. Flow cytometry analysis suggested that the stem extract might suppress H838 cell proliferation by inducing G2 cell cycle arrest, thereby inhibiting carcinoma cell proliferation. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) enabled the tentative identification of the 15 most abundant compounds in the stem extract of N. miranda. Notably, the extract showed a potent inhibition of the human RPA32 protein (huRPA32), critical for DNA replication, suggesting a novel mechanism for its anticancer action. Molecular docking studies further substantiated the interaction between the extract and huRPA32, highlighting bioactive compounds, especially the two most abundant constituents, stigmast-5-en-3-ol and plumbagin, as potential inhibitors of huRPA32's DNA-binding activity, offering promising avenues for cancer therapy. Overall, our findings position the stem extract of N. miranda as a promising source of natural compounds for anticancer therapeutics and anti-skin-aging treatments, warranting further investigation into its molecular mechanisms and potential clinical applications.
Keywords: AntoDock; GC–MS analysis; H838 lung carcinoma; Nepenthes; RPA; anti-skin aging; anticancer; elastase; plumbagin; stigmast-5-en-3-ol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
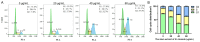
References
-
- Meng Y., Sun H., Wang S., Yang H., Kong F.S. Treatment-Related Pneumonitis of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Plus Thoracic Radiation Therapy in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024;118:415–426. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.09.009. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

