Overexpression of RAD54L attenuates osteoarthritis by suppressing the HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway: Bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation
- PMID: 38593124
- PMCID: PMC11003635
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298575
Overexpression of RAD54L attenuates osteoarthritis by suppressing the HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway: Bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation
Abstract
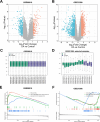
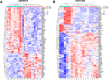
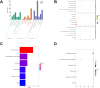
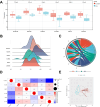
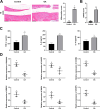
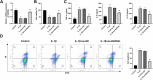
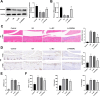
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a widespread chronic, progressive, degenerative joint disease that causes pain and disability. Current treatments for OA have limited effectiveness and new biomarkers need to be identified. Bioinformatics analysis was conducted to explore differentially expressed genes and DNA repair/recombination protein 54 L (RAD54L) was selected. We firstly overexpressed RAD54L in interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-induced human articular chondrocytes or in OA rats to investigate its effect on OA. Chondrocyte viability and apoptotic rate were measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 and flow cytometry, respectively. Then we evaluated OA severity in vivo by Hematoxylin-eosin staining and Osteoarthritis Research Society International standards. The expression of inflammatory mediators was tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Finally, western blot was performed to determine the relative expression level of hypoxia-inducible factors 1α (HIF-1α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Overexpression of RAD54L promoted cell viability and attenuated apoptosis in IL-1β-induced human chondrocytes. A lower Osteoarthritis Research Society International score and a remarkable alleviation of chondrocyte disordering and infiltration of inflammatory cells were found in cartilage tissues of OA rats after overexpressing RAD54L. The inflammatory response induced by OA was decreased by RAD54L overexpression in vitro and in vivo. In addition, RAD54L overexpression decreased the relative expression level of HIF-1α and VEGF. Overexpression of RAD54L could attenuate OA by suppressing the HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway, indicating that RAD54L may be a potential treatment target for OA.
Copyright: © 2024 Li et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
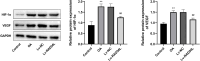
Similar articles
-
Aucubin Protects Chondrocytes Against IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis In Vitro And Inhibits Osteoarthritis In Mice Model.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Oct 9;13:3529-3538. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S210220. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31631977 Free PMC article.
-
FBW7 regulates HIF-1α/VEGF pathway in the IL-1β induced chondrocytes degeneration.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Jun;24(11):5914-5924. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202006_21484. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32572904
-
Vitexin alleviates interleukin-1β-induced inflammatory responses in chondrocytes from osteoarthritis patients: Involvement of HIF-1α pathway.Scand J Immunol. 2019 Aug;90(2):e12773. doi: 10.1111/sji.12773. Epub 2019 May 22. Scand J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31055848
-
Insights on Molecular Mechanisms of Chondrocytes Death in Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 20;17(12):2146. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122146. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27999417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of HIF-1α in hypoxic metabolic reprogramming in osteoarthritis.Pharmacol Res. 2025 Mar;213:107649. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107649. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Pharmacol Res. 2025. PMID: 39947451 Review.
Cited by
-
Cartilage Homeostasis under Physioxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9398. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179398. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273346 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

