Rab7-dependent regulation of goblet cell protein CLCA1 modulates gastrointestinal homeostasis
- PMID: 38593125
- PMCID: PMC11003743
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.89776
Rab7-dependent regulation of goblet cell protein CLCA1 modulates gastrointestinal homeostasis
Abstract
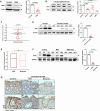
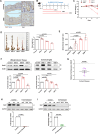
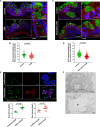
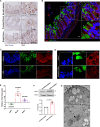
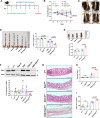
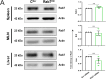
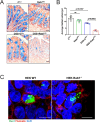
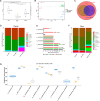
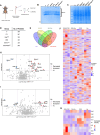
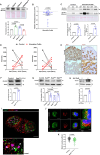
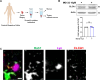
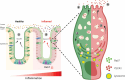
Inflammation in ulcerative colitis is typically restricted to the mucosal layer of distal gut. Disrupted mucus barrier, coupled with microbial dysbiosis, has been reported to occur prior to the onset of inflammation. Here, we show the involvement of vesicular trafficking protein Rab7 in regulating the colonic mucus system. We identified a lowered Rab7 expression in goblet cells of colon during human and murine colitis. In vivo Rab7 knocked down mice (Rab7KD) displayed a compromised mucus layer, increased microbial permeability, and depleted gut microbiota with enhanced susceptibility to dextran sodium-sulfate induced colitis. These abnormalities emerged owing to altered mucus composition, as revealed by mucus proteomics, with increased expression of mucin protease chloride channel accessory 1 (CLCA1). Mechanistically, Rab7 maintained optimal CLCA1 levels by controlling its lysosomal degradation, a process that was dysregulated during colitis. Overall, our work establishes a role for Rab7-dependent control of CLCA1 secretion required for maintaining mucosal homeostasis.
Keywords: CLCA1; Rab7 GTPase; goblet cells; human; immunology; inflammation; inflammatory bowel disease; mouse; mucus; ulcerative colitis.
© 2023, Gaur et al.
Conflict of interest statement
PG, YR, BS, MM, VF, GM, AS, SC, ST, SY, AP, YM, AB, VA, CS No competing interests declared
Figures



Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.02.13.528320
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.89776.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.89776.2
References
-
- BasuRay S, Mukherjee S, Romero EG, Seaman MNJ, Wandinger-Ness A. Rab7 mutants associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease cause delayed growth factor receptor transport and altered endosomal and nuclear signaling. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2013;288:1135–1149. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.417766. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

