Prediction of cross-border spread of the COVID-19 pandemic: A predictive model for imported cases outside China
- PMID: 38593140
- PMCID: PMC11003692
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301420
Prediction of cross-border spread of the COVID-19 pandemic: A predictive model for imported cases outside China
Abstract
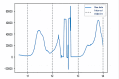
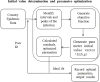
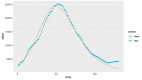
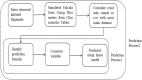
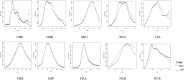
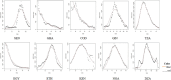
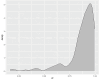
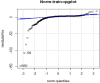
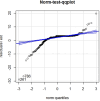
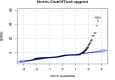
The COVID-19 pandemic has been present globally for more than three years, and cross-border transmission has played an important role in its spread. Currently, most predictions of COVID-19 spread are limited to a country (or a region), and models for cross-border transmission risk assessment remain lacking. Information on imported COVID-19 cases reported from March 2020 to June 2022 was collected from the National Health Commission of China, and COVID-19 epidemic data of the countries of origin of the imported cases were collected on data websites such as WHO and Our World in Data. It is proposed to establish a prediction model suitable for the prevention and control of overseas importation of COVID-19. Firstly, the SIR model was used to fit the epidemic infection status of the countries where the cases were exported, and most of the r2 values of the fitted curves obtained were above 0.75, which indicated that the SIR model could well fit different countries and the infection status of the region. After fitting the epidemic infection status data of overseas exporting countries, on this basis, a SIR-multiple linear regression overseas import risk prediction combination model was established, which can predict the risk of overseas case importation, and the established overseas import risk model overall P <0.05, the adjusted R2 = 0.7, indicating that the SIR-multivariate linear regression overseas import risk prediction combination model can obtain better prediction results. Our model effectively estimates the risk of imported cases of COVID-19 from abroad.
Copyright: © 2024 Wang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Risk assessment of global COVID-19 imported cases into China].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Oct 10;41(10):1582-1587. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200415-00577. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32455514 Chinese.
-
Travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 5;10:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 25;3:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. PMID: 33502002 Updated.
-
International travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 25;3(3):CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33763851 Free PMC article.
-
Should we remain hopeful? The key 8 weeks: spatiotemporal epidemic characteristics of COVID-19 in Sichuan Province and its comparative analysis with other provinces in China and global epidemic trends.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Nov 5;20(1):807. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05494-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33153445 Free PMC article.
-
[Management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): experiences from imported malaria control in China].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020 Mar 18;32(2):113-118. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2020063. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32458598 Chinese.
References
-
- Organization WH. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard | WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard With Vaccination Data https://covid19.who.int/
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

