Hepatic Topology of Glycosphingolipids in Schistosoma mansoni-Infected Hamsters
- PMID: 38594017
- PMCID: PMC11044111
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05846
Hepatic Topology of Glycosphingolipids in Schistosoma mansoni-Infected Hamsters
Abstract
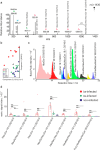
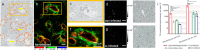
Schistosomiasis is a neglected tropical disease caused by worm parasites of the genus Schistosoma. Upon infection, parasite eggs can lodge inside of host organs like the liver. This leads to granuloma formation, which is the main cause of the pathology of schistosomiasis. To better understand the different levels of host-pathogen interaction and pathology, our study focused on the characterization of glycosphingolipids (GSLs). For this purpose, GSLs in livers of infected and noninfected hamsters were studied by combining high-spatial-resolution atmospheric-pressure scanning microprobe matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (AP-SMALDI MSI) with nanoscale hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (nano-HILIC MS/MS). Nano-HILIC MS/MS revealed 60 GSL species with a distinct saccharide and ceramide composition. AP-SMALDI MSI measurements were conducted in positive- and negative-ion mode for the visualization of neutral and acidic GSLs. Based on nano-HILIC MS/MS results, we discovered no downregulated but 50 significantly upregulated GSLs in liver samples of infected hamsters. AP-SMALDI MSI showed that 44 of these GSL species were associated with the granulomas in the liver tissue. Our findings suggest an important role of GSLs during granuloma formation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): B.S. and C.G.G are consultants of TransMIT GmbH, Giessen, Germany. All others declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Spengler B.; Hubert M.; Kaufmann R.. MALDI ion imaging and biological ion imaging with a new scanning UV-laser microprobe. Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, 1994; Vol. 1040.
-
- Koestler M.; Kirsch D.; Hester A.; Leisner A.; Guenther S.; Spengler B. A high-resolution scanning microprobe matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization ion source for imaging analysis on an ion trap/Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 3275–3285. 10.1002/rcm.3733. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bien T.; Perl M.; Machmüller A. C.; Nitsche U.; Conrad A.; Johannes L.; Müthing J.; Soltwisch J.; Janssen K.-P.; Dreisewerd K. MALDI-2 Mass Spectrometry and Immunohistochemistry Imaging of Gb3Cer, Gb4Cer, and Further Glycosphingolipids in Human Colorectal Cancer Tissue. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7096–7105. 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00480. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

