Evaluating the effectiveness of sulfidated nano zerovalent iron and sludge co-application for reducing metal mobility in contaminated soil
- PMID: 38594335
- PMCID: PMC11004183
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-59059-7
Evaluating the effectiveness of sulfidated nano zerovalent iron and sludge co-application for reducing metal mobility in contaminated soil
Abstract
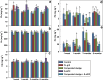
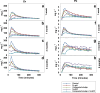
Sewage sludge has long been applied to soils as a fertilizer yet may be enriched with leachable metal(loid)s and other pollutants. Sulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron (S-nZVI) has proven effective at metal sorption; however, risks associated with the use of engineered nanoparticles cannot be neglected. This study investigated the effects of the co-application of composted sewage sludge with S-nZVI for the stabilization of Cd, Pb, Fe, Zn. Five treatments (control, Fe grit, composted sludge, S-nZVI, composted sludge and S-nZVI), two leaching fluids; synthetic precipitation leaching procedure (SPLP) and toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) fluid were used, samples were incubated at different time intervals of 1 week, 1, 3, and 6 months. Fe grit proved most efficient in reducing the concentration of extractable metals in the batch experiment; the mixture of composted sludge and S-nZVI was the most effective in reducing the leachability of metals in the column systems, while S-nZVI was the most efficient for reducing about 80% of Zn concentration in soil solution. Thus, the combination of two amendments, S-nZVI incorporated with composted sewage sludge and Fe grit proved most effective at reducing metal leaching and possibly lowering the associated risks. Future work should investigate the longer-term efficiency of this combination.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Usman K, et al. Sewage sludge: An important biological resource for sustainable agriculture and its environmental implications. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2012;03:1708–1721. doi: 10.4236/ajps.2012.312209. - DOI
-
- Li XQ, Brown DG, Zhang WX. Stabilization of biosolids with nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) J. Nanopart. Res. 2007;9:233–243. doi: 10.1007/s11051-006-9187-1. - DOI
-
- Đurđević D, Žiković S, Blecich P. Sustainable sewage sludge management technologies selection based on techno–economic–environmental criteria: Case study of Croatia. Energies. 2022;15:3941. doi: 10.3390/en15113941. - DOI
-
- Rorat A, Courtois P, Vandenbulcke F, Lemiere S. Sanitary and environmental aspects of sewage sludge management. In: Prasad MN, de Campos Favas PJ, Vithanage M, Mohan SV, editors. Industrial and Municipal Sludge: Emerging Concerns and Scope for Resource Recovery. Butterworth-Heinemann; 2019. pp. 155–180.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

