Characteristics and whole-genome analysis of a novel Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato bacteriophage D6 isolated from a karst cave
- PMID: 38594490
- PMCID: PMC11139720
- DOI: 10.1007/s11262-024-02064-9
Characteristics and whole-genome analysis of a novel Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato bacteriophage D6 isolated from a karst cave
Abstract
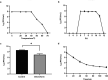
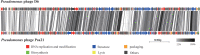
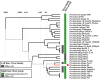
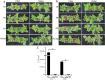
Pseudomonas syringae is a gram-negative plant pathogen that infects plants such as tomato and poses a threat to global crop production. In this study, a novel lytic phage infecting P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000, named phage D6, was isolated and characterized from sediments in a karst cave. The latent period of phage D6 was found to be 60 min, with a burst size of 16 plaque-forming units per cell. Phage D6 was stable at temperatures between 4 and 40 °C but lost infectivity when heated to 70 °C. Its infectivity was unaffected at pH 6-10 but became inactivated at pH ≤ 5 or ≥ 12. The genome of phage D6 is a linear double-stranded DNA of 307,402 bp with a G + C content of 48.43%. There is a codon preference between phage D6 and its host, and the translation of phage D6 gene may not be entirely dependent on the tRNA library provided by the host. A total of 410 open reading frames (ORFs) and 14 tRNAs were predicted in its genome, with 92 ORFs encoding proteins with predicted functions. Phage D6 showed low genomic similarity to known phage genomes in the GenBank and Viral sequence databases. Genomic and phylogenetic analyses revealed that phage D6 is a novel phage. The tomato plants were first injected with phage D6, and subsequently with Pst DC3000, using the foliar spraying and root drenching inoculum approach. Results obtained after 14 days indicated that phage D6 inoculation decreased P. syringae-induced symptoms in tomato leaves and inhibited the pathogen's growth in the leaves. The amount of Pst DC3000 was reduced by 150- and 263-fold, respectively. In conclusion, the lytic phage D6 identified in this study belongs to a novel phage within the Caudoviricetes class and has potential for use in biological control of plant diseases.
Keywords: Caudoviricetes; Pseudomonas syringae; Bacteriophage; Biocontrol; Karst cave; Plant pathogen; Whole genome analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared that there are no conflicts.
Figures

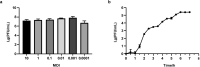




Similar articles
-
Complete genome sequence of Phobos: a novel bacteriophage with unusual genomic features that infects Pseudomonas syringae.Arch Virol. 2020 Jun;165(6):1485-1488. doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04618-2. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Arch Virol. 2020. PMID: 32248294
-
Isolation of the Novel Phage PHB09 and Its Potential Use against the Plant Pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae.Viruses. 2021 Nov 14;13(11):2275. doi: 10.3390/v13112275. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34835081 Free PMC article.
-
In planta interactions of a novel bacteriophage against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jun;107(11):3801-3815. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12493-5. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37074382 Free PMC article.
-
The Bacteriophage Pf-10-A Component of the Biopesticide "Multiphage" Used to Control Agricultural Crop Diseases Caused by Pseudomonas syringae.Viruses. 2021 Dec 27;14(1):42. doi: 10.3390/v14010042. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 35062246 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000: a model pathogen for probing disease susceptibility and hormone signaling in plants.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2013;51:473-98. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102321. Epub 2013 May 31. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2013. PMID: 23725467 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization and genomic analysis of a lytic Stenotrophomonas maltophilia short-tailed phage A1432 revealed a new genus of the family Mesyanzhinovviridae.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 27;15:1400700. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1400700. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38993489 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analysis of the novel Stenotrophomonas phage vB_Srh_LBjhp91a, isolated from a Karst cave in China.Arch Virol. 2025 May 29;170(7):142. doi: 10.1007/s00705-025-06329-y. Arch Virol. 2025. PMID: 40439743
-
Sustainable and innovative biological control strategies against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato, Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. phaseolicola and Xanthomonas spp. affecting vegetable crops: a review.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Apr 30;16:1536152. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1536152. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40370367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Korniienko N, Kharina A, Zrelovs N, Jindřichová B, Moravec T, Budzanivska I, et al. Isolation and characterization of two lytic phages efficient against phytopathogenic bacteria from Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas Genera. Front Microbiol. 2022;25(13):853593. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.853593. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

