Insulin eye drops improve corneal wound healing in STZ-induced diabetic mice by regulating corneal inflammation and neuropeptide release
- PMID: 38594682
- PMCID: PMC11003036
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-024-03436-3
Insulin eye drops improve corneal wound healing in STZ-induced diabetic mice by regulating corneal inflammation and neuropeptide release
Abstract
Introduction: In recent years, insulin eye drops have attracted increasing attention from researchers and ophthalmologists. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy and possible mechanism of action of insulin eye drops in diabetic mice with corneal wounds.
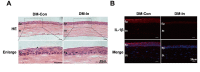
Methods: A type 1 diabetes model was induced, and a corneal epithelial injury model of 2.5 mm was established. We used corneal fluorescein staining, hematoxylin-eosin (H-E) staining and the Cochet-Bonnet esthesiometer to examine the process of wound healing. Subsequently, the expression levels of Ki-67, IL-1β, β3-tubulin and neuropeptides, including substance P (SP) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), were examined at 72 h after corneal injury.
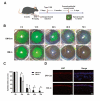
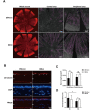
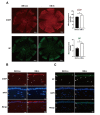
Results: Fluorescein staining demonstrated an acceleration of the recovery of corneal epithelial injury in diabetic mice compared with the saline treatment, which was further evidenced by the overexpression of Ki-67. Moreover, 72 h of insulin application attenuated the expression of inflammatory cytokines and neutrophil infiltration. Remarkably, the results demonstrated that topical insulin treatment enhanced the density of corneal epithelial nerves, as well as neuropeptide SP and CGRP release, in the healing cornea via immunofluorescence staining.
Conclusions: Our results indicated that insulin eye drops may accelerate corneal wound healing and decrease inflammatory responses in diabetic mice by promoting nerve regeneration and increasing levels of neuropeptides SP and CGRP.
Keywords: Diabetic keratopathy; Inflammation; Insulin eye drops; Nerve regeneration; Neuropeptides.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resolvin D1 promotes corneal epithelial wound healing and restoration of mechanical sensation in diabetic mice.Mol Vis. 2018 Apr 1;24:274-285. eCollection 2018. Mol Vis. 2018. PMID: 29643724 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of corneal sensitivity, calcitonin gene-related peptide-positive nerves, and increased wound healing induced by pigment epithelial-derived factor plus docosahexaenoic acid after experimental surgery.Arch Ophthalmol. 2012 Jan;130(1):76-83. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2011.287. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Arch Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 21911652
-
IL-20 promotes epithelial healing of the injured mouse cornea.Exp Eye Res. 2017 Jan;154:22-29. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27818315 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental modeling of cornea wound healing in diabetes: clinical applications and beyond.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019 Nov 27;7(1):e000779. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-000779. eCollection 2019. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019. PMID: 31803484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of sensory neuropathy and inflammation on epithelial wound healing in diabetic corneas.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022 Jul;89:101039. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101039. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34991965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mucoadhesive nanofibers for ocular drug delivery: mechanisms, design strategies, and applications.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jun 25. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01894-w. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40562965
-
Dexmedetomidine ameliorates diabetic intestinal injury by promoting the polarization of M2 macrophages through the MMP23B pathway.World J Diabetes. 2024 Sep 15;15(9):1962-1978. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i9.1962. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 39280187 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Insulin Eye Drops in Neurotrophic Keratopathy: A Comprehensive Review.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 7;13(7):1657. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071657. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722729 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

