Recommendations for quantitative cerebral perfusion MRI using multi-timepoint arterial spin labeling: Acquisition, quantification, and clinical applications
- PMID: 38594906
- PMCID: PMC11142882
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.30091
Recommendations for quantitative cerebral perfusion MRI using multi-timepoint arterial spin labeling: Acquisition, quantification, and clinical applications
Abstract
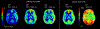
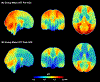
Accurate assessment of cerebral perfusion is vital for understanding the hemodynamic processes involved in various neurological disorders and guiding clinical decision-making. This guidelines article provides a comprehensive overview of quantitative perfusion imaging of the brain using multi-timepoint arterial spin labeling (ASL), along with recommendations for its acquisition and quantification. A major benefit of acquiring ASL data with multiple label durations and/or post-labeling delays (PLDs) is being able to account for the effect of variable arterial transit time (ATT) on quantitative perfusion values and additionally visualize the spatial pattern of ATT itself, providing valuable clinical insights. Although multi-timepoint data can be acquired in the same scan time as single-PLD data with comparable perfusion measurement precision, its acquisition and postprocessing presents challenges beyond single-PLD ASL, impeding widespread adoption. Building upon the 2015 ASL consensus article, this work highlights the protocol distinctions specific to multi-timepoint ASL and provides robust recommendations for acquiring high-quality data. Additionally, we propose an extended quantification model based on the 2015 consensus model and discuss relevant postprocessing options to enhance the analysis of multi-timepoint ASL data. Furthermore, we review the potential clinical applications where multi-timepoint ASL is expected to offer significant benefits. This article is part of a series published by the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM) Perfusion Study Group, aiming to guide and inspire the advancement and utilization of ASL beyond the scope of the 2015 consensus article.
Keywords: arterial spin labeling; arterial transit time; cerebral blood flow; multi‐timepoint; perfusion.
© 2024 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
DB received research grant support from GE Healthcare. MAC receives royalties from the commercial licensing of FSL and is an employee of, and holds equity in, Quantified Imaging Ltd. XG is a founder, shareholder and employee of Gold Standard Phantoms and a consultant at Bioxydyn. TO works as an ad hoc consultant for SBGNeuro Ltd. MJPvO receives research support from Philips. MS received consultation fees from Bracco and a speaker fee from Instituzione Internazionale Menarini (both paid to Erasmus MC). DJW is a shareholder of Hura Imaging, INC. GZ receives grant support from GE Healthcare and Bayer Healthcare and has equity interest in Subtle Medical, Inc.
Figures




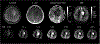
References
-
- Martin SZ, Madai VI, von Samson-Himmelstjerna FC, et al. 3D GRASE Pulsed Arterial Spin Labeling at Multiple Inflow Times in Patients with Long Arterial Transit Times: Comparison with Dynamic Susceptibility-Weighted Contrast-Enhanced MRI at 3 Tesla. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35(3):392–401. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 EB031771/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG070318/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 NS102884/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EP/S021507/1/Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council
- K01-AG070318/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-NS123025/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 539208/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 203139/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 220204/Z/20/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- PI21/00578/Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation
- R01 NS123025/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-EB025220/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB025220/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 AG072972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB033210/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01EB033210/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 016.160.351/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- U01 CA207091/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00-NS-102884/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

