MicroRNA-502-3p regulates GABAergic synapse function in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 38595288
- PMCID: PMC11168514
- DOI: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01064
MicroRNA-502-3p regulates GABAergic synapse function in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
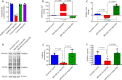
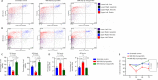
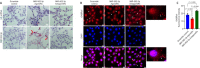
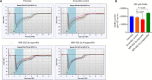
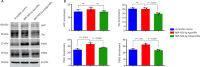
JOURNAL/nrgr/04.03/01300535-202412000-00026/figure1/v/2024-04-08T165401Z/r/image-tiff Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic neurons, the most abundant inhibitory neurons in the human brain, have been found to be reduced in many neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease and Alzheimer's disease-related dementia. Our previous study identified the upregulation of microRNA-502-3p (miR-502-3p) and downregulation of GABA type A receptor subunit α-1 in Alzheimer's disease synapses. This study investigated a new molecular relationship between miR-502-3p and GABAergic synapse function. In vitro studies were performed using the mouse hippocampal neuronal cell line HT22 and miR-502-3p agomiRs and antagomiRs. In silico analysis identified multiple binding sites of miR-502-3p at GABA type A receptor subunit α-1 mRNA. Luciferase assay confirmed that miR-502-3p targets the GABA type A receptor subunit α-1 gene and suppresses the luciferase activity. Furthermore, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, miRNA in situ hybridization, immunoblotting, and immunostaining analysis confirmed that overexpression of miR-502-3p reduced the GABA type A receptor subunit α-1 level, while suppression of miR-502-3p increased the level of GABA type A receptor subunit α-1 protein. Notably, as a result of the overexpression of miR-502-3p, cell viability was found to be reduced, and the population of necrotic cells was found to be increased. The whole cell patch-clamp analysis of human-GABA receptor A-α1/β3/γ2L human embryonic kidney (HEK) recombinant cell line also showed that overexpression of miR-502-3p reduced the GABA current and overall GABA function, suggesting a negative correlation between miR-502-3p levels and GABAergic synapse function. Additionally, the levels of proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease were high with miR-502-3p overexpression and reduced with miR-502-3p suppression. The present study provides insight into the molecular mechanism of regulation of GABAergic synapses by miR-502-3p. We propose that micro-RNA, in particular miR-502-3p, could be a potential therapeutic target to modulate GABAergic synapse function in neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease and Alzheimer's disease-related dementia.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Neural Regeneration Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Calvo‐Flores Guzmán B, Vinnakota C, Govindpani K, Waldvogel HJ, Faull RL, Kwakowsky A. The GABAergic system as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2018;146:649–669. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti M, Saha T. Identification of human microRNAs targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa genes by an in silico hybridization method. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;34:101110.
-
- Davis JB, Maher P. Protein kinase C activation inhibits glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in a neuronal cell line. Brain Res. 1994;652:169–173. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

