Hematological and blood biochemistry parameters as prognostic indicators of survival in canine multicentric lymphoma treated with COP and L-COP protocols
- PMID: 38595652
- PMCID: PMC11000476
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.344-355
Hematological and blood biochemistry parameters as prognostic indicators of survival in canine multicentric lymphoma treated with COP and L-COP protocols
Abstract
Background and aim: Hematological and blood chemistry parameters are crucial for evaluating and monitoring canine multicentric lymphoma during chemotherapy. Pre-treatment hematological and blood chemistry parameters can be used as prognostic survival outcomes for this disease. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effect of hematological and blood chemistry parameters pre-treatment and 4 weeks post-treatment on the survival outcomes of dogs treated with either a combination of cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisolone (COP) or a combination of COP with L-asparaginase (L-COP) protocols.
Materials and methods: We conducted a retrospective study. Medical records and hematological and blood chemistry parameters of 41 dogs with multicentric lymphoma treated with L-COP (n = 26) and the COP protocols (n = 15) were obtained from the hospital information system. Most cases were classified as high-grade lymphoma based on the Kiel cytological classification. The effects of hematological and blood chemistry parameters on survival outcomes were investigated using the Cox proportional hazard regression model. The median survival time (MST) for each hematological and blood chemistry parameter affecting survival outcome was established and compared using the Kaplan-Meier product limit method with the log-rank test.
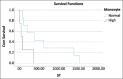
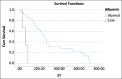
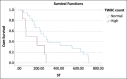
Results: Dogs with high-grade multicentric lymphoma that were treated with the COP protocol and had monocytosis at pre-treatment had a significantly shorter MST than dogs with normal monocyte counts (p = 0.033). In addition, dogs with azotemia, both pre-treatment and 4 weeks post-treatment, had a significantly shorter MST than dogs with normal serum creatinine levels (p = 0.012). Dogs with high-grade multicentric lymphoma treated with the L-COP protocol who had hypoalbuminemia (serum albumin concentration <2.5 mg/dL) at both pre-treatment and 4 weeks post-treatment had a significantly shorter MST than dogs with normal serum albumin levels (p < 0.001). Furthermore, dogs with leukocytosis at 4 weeks post-treatment had a significantly shorter MST than those with a normal total white blood cell count (p = 0.024).
Conclusion: Serum albumin level can serve as a simple negative prognostic indicator of survival outcomes in dogs with high-grade multicentric lymphoma treated with the L-COP protocol. Dogs with hypoalbuminemia pre-treatment and 4 weeks post-treatment tended to have a shorter MST than those with normal serum albumin concentrations.
Keywords: anti-cancer; chemotherapy; dogs; hypoalbuminemia; multicentric lymphoma; prognosis; retrospective study; survival outcomes.
Copyright: © Sutthigran, et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Vail D.M, Thamm D.H, Liptak J.M. Hematopoietic tumors. In:Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Elsevier, St. Louis, Missouri. 2019:688–772.
-
- Merlo D.F, Rossi L, Pellegrino C, Ceppi M, Cardellino U, Capurro C. Cancer incidence in pet dogs:Findings of the animal tumor registry of Genoa, Italy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2008;22(4):976–984. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R.L, Miller K.D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Valli V.E, Kass P.H, San Myint M, Scott F. Canine lymphomas:Association of classification type, disease stage, tumor subtype, mitotic rate, and treatment with survival. Vet. Pathol. 2013;50(5):738–748. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
