The characteristic and prognostic role of blood inflammatory markers in patients with Huntington's disease from China
- PMID: 38595854
- PMCID: PMC11002148
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1374365
The characteristic and prognostic role of blood inflammatory markers in patients with Huntington's disease from China
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to elucidate the role of peripheral inflammation in Huntington's disease (HD) by examining the correlation of peripheral inflammatory markers with clinical manifestations and disease prognosis.
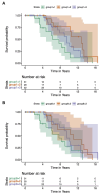
Methods: This investigation involved 92 HD patients and 92 matched healthy controls (HCs). We quantified various peripheral inflammatory markers and calculated their derived metrics including neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), and systemic immune-inflammation index (SII). Clinical assessments spanning cognitive, motor, and disease severity were administered. Comparative analysis of inflammatory markers and clinical correlations between HD and controls was performed. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox regression model were used to assess the effect of inflammatory markers on survival.
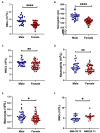
Results: The study revealed that HD patients had significantly reduced lymphocyte counts, and LMR. Conversely, NLR, PLR, and SII were elevated compared to HCs. Lymphocyte levels inversely correlated with the age of onset and monocyte levels inversely correlated with the UHDRS-total functional capacity (TFC) scores. After adjusting for age, sex, and CAG repeat length, lymphocyte count, NLR, PLR, and SII were significantly correlated with the progression rate of TFC scores. Elevated levels of white blood cells and monocytes were associated with an increased risk of disability and mortality in the HD cohort.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that HD patients display a distinct peripheral inflammatory profile with increased NLR, PLR, and SII levels compared to HCs. The peripheral inflammation appears to be linked with accelerated disease progression and decreased survival in HD.
Keywords: Huntington’s disease; biomarkers; peripheral inflammatory; prognosis; progression.
Copyright © 2024 Xia, Cheng, Zhang, Ma, Fu, Yang, Zhang, Burgunder and Shang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
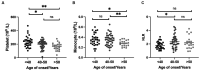
Similar articles
-
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT DERIVED INFLAMMATORY BIOMARKERS IN PATIENTS WITH HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES.Georgian Med News. 2020 May;(302):39-44. Georgian Med News. 2020. PMID: 32672687
-
The prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and systemic immune-inflammation index on short- and long-term outcome following surgery for spinal metastases.J Neurosurg Spine. 2023 Dec 29;40(4):475-484. doi: 10.3171/2023.10.SPINE23851. Print 2024 Apr 1. J Neurosurg Spine. 2023. PMID: 38157531
-
[Relationship between preoperative inflammatory indexes and prognosis of patients with rectal cancer and establishment of prognostic nomogram prediction model].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022 May 23;44(5):402-409. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200630-00612. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35615796 Chinese.
-
The potential predictive value and relationship of blood-based inflammatory markers with the clinical symptoms of Han Chinese patients with first-episode adolescent-onset schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 3;15:1431350. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1431350. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39290303 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 as a marker of Huntington's disease progression: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023 May 5;30:100635. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2023.100635. eCollection 2023 Jul. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023. PMID: 37215308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers as predictors of pain in sequential bilateral phacoemulsification for age-related cataract.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 11;12:1626533. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1626533. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40718414 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers Across Multiple Antiseizure Medications: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of 1782 Patients.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 22;14(15):5190. doi: 10.3390/jcm14155190. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40806813 Free PMC article.

