Quercetin reshapes gut microbiota homeostasis and modulates brain metabolic profile to regulate depression-like behaviors induced by CUMS in rats
- PMID: 38595919
- PMCID: PMC11002179
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1362464
Quercetin reshapes gut microbiota homeostasis and modulates brain metabolic profile to regulate depression-like behaviors induced by CUMS in rats
Abstract
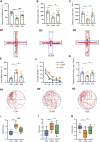
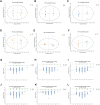
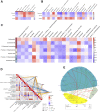
Quercetin, an abundant flavonoid compound in plants, is considered a novel antidepressant; however, its mechanisms of action are poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects of quercetin on chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS)-induced depression-like behaviors in rats and explore the underlying mechanisms by combining untargeted metabolomics and 16S rRNA sequencing analysis of brain tissue metabolites and gut microbiota. Gut microbiota analysis revealed that at the phylum level, quercetin reduced Firmicutes and the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratio and enhanced Cyanobacteria. At the genus level, quercetin downregulated 6 and upregulated 14 bacterial species. Metabolomics analysis revealed that quercetin regulated multiple metabolic pathways, including glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, sphingolipid metabolism, the pentose phosphate pathway, and coenzyme A biosynthesis. This modulation leads to improvements in depression-like phenotypes, anxiety-like phenotypes, and cognitive function, highlighting the therapeutic potential of quercetin in treating depression.
Keywords: brain metabolomics; depression; gut microbiota; microbiota-gut-brain axis; quercetin.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Yan, Zhang, Xu, Wu, Yao, Li, Yan and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

