Learning algorithms for identification of whisky using portable Raman spectroscopy
- PMID: 38595930
- PMCID: PMC11002798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100729
Learning algorithms for identification of whisky using portable Raman spectroscopy
Abstract
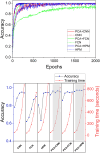
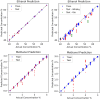
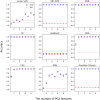
Reliable identification of high-value products such as whisky is vital due to rising issues of brand substitution and quality control in the industry. We have developed a novel framework that can perform whisky analysis directly from raw spectral data with no human intervention by integrating machine learning models with a portable Raman device. We demonstrate that machine learning models can achieve over 99% accuracy in brand or product identification across twenty-eight commercial samples. To demonstrate the flexibility of this approach, we utilized the same algorithms to quantify ethanol concentrations, as well as measuring methanol levels in spiked whisky samples. To demonstrate the potential use of these algorithms in a real-world environment we tested our algorithms on spectral measurements performed through the original whisky bottle. Through the bottle measurements are facilitated by a beam geometry hitherto not applied to whisky brand identification in conjunction with machine learning. Removing the need for decanting greatly enhances the practicality and commercial potential of this technique, enabling its use in detecting counterfeit or adulterated spirits and other high-value liquids. The techniques established in this paper aim to function as a rapid and non-destructive initial screening mechanism for detecting falsified and tampered spirits, complementing more comprehensive and stringent analytical methods.
Keywords: Brand identification; Machine learning; Raman spectroscopy; Whisky.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-Destructive and Non-Invasive Measurement of Ethanol and Toxic Alcohol Strengths in Beverages and Spirits Using Portable Raman Spectroscopy.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 13;13(1):135. doi: 10.3390/bios13010135. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671970 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Authentication of Plant-Based Milk Alternatives by Coupling Portable Raman Spectroscopy with Machine Learning.J AOAC Int. 2025 Mar 12:qsaf022. doi: 10.1093/jaoacint/qsaf022. Online ahead of print. J AOAC Int. 2025. PMID: 40073253
-
Through-bottle whisky sensing and classification using Raman spectroscopy in an axicon-based backscattering configuration.Anal Methods. 2020 Oct 7;12(37):4572-4578. doi: 10.1039/d0ay01101k. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Anal Methods. 2020. PMID: 33001069
-
Chemical composition analysis and authentication of whisky.J Sci Food Agric. 2015 Aug 30;95(11):2159-66. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6960. Epub 2014 Nov 13. J Sci Food Agric. 2015. PMID: 25315338 Review.
-
Analysis and comparison of machine learning methods for blood identification using single-cell laser tweezer Raman spectroscopy.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2022 Sep 5;277:121274. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2022.121274. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2022. PMID: 35500354 Review.
References
-
- Ashok Praveen C., Praveen Bavishna B., Dholakia K. Near infrared spectroscopic analysis of single malt Scotch whisky on an optofluidic chip. 2011;19(23):22982–22992. - PubMed
-
- Ashok Praveen C., Praveen Bavishna B., Dholakia Kishan. Optofluidic Raman sensor for simultaneous detection of the toxicity and quality of alcoholic beverages. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013;44(6):795–797.
-
- Chaudhry P.E., Zimmerman A., Peters J.R., Cordell V.V. Preserving intellectual property rights: managerial insight into the escalating counterfeit market quandary. Bus. Horiz. 2009;52(1):57–66.
-
- Chollet F. Simon and Schuster; 2017. Deep Learning with Python.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

