New developments in the imaging of lung cancer
- PMID: 38595936
- PMCID: PMC11003524
- DOI: 10.1183/20734735.0176-2023
New developments in the imaging of lung cancer
Abstract
Radiological and nuclear medicine methods play a fundamental role in the diagnosis and staging of patients with lung cancer. Imaging is essential in the detection, characterisation, staging and follow-up of lung cancer. Due to the increasing evidence, low-dose chest computed tomography (CT) screening for the early detection of lung cancer is being introduced to the clinical routine in several countries. Radiomics and radiogenomics are emerging fields reliant on artificial intelligence to improve diagnosis and personalised risk stratification. Ultrasound- and CT-guided interventions are minimally invasive methods for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary malignancies. In this review, we put more emphasis on the new developments in the imaging of lung cancer.
Copyright ©ERS 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Á.D. Tárnoki and D.L. Tárnoki were funded by the Bólyai scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences; and ÚNKP-20-5 and ÚNKP-21-5 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology from the source of the National Research, Development, and Innovation Fund; and by the Hungarian National Laboratory (under the National Tumourbiology Laboratory project, NLP-17). M. Dąbrowska has nothing to disclose. M. Knetki-Wróblewska's conflicts of interest include being an invited speaker of MSD, BMS, Roche, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Takeda, Pfizer, and receiving travel grants from MSD, Takeda, AstraZeneca and Pfizer. A. Frille reports a postdoctoral fellowship “MetaRot program” (clinician scientist program) from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany (FKZ 01EO1501, IFB Adiposity Diseases), a research grant from the Mitteldeutsche Gesellschaft für Pneumologie (MDGP) e.V. (2018-MDGP-PA-002), a junior research grant from the Medical Faculty, University of Leipzig (934100-012), Germany, a graduate fellowship from the Novartis-Stiftung für therapeutische Forschung and funding from the “PETictCAC” project (ERA-PerMed_324), which was funded with tax funds on the basis of the budget passed by the Saxon State Parliament (Germany) under the frame of ERA PerMed (Horizon 2020). H. Stubbs reports grants from Janssen-Cliag Ltd (funding support for unrelated study (2021)); and support for attending meetings and/or travel from Janssen-Cliag Ltd (support for attending ERS 2022, ERS 2021 and ATS 2021) and AOP (support for attending ERS 2023 and PH Academy 2023). K.G. Blyth reports grants from Rocket Medical and RS Oncology (research funding to institution); and other financial or non-financial interests as co-investigator of PREDICT-Meso international accelerator. A.D. Juul reports grants from the Danish Cancer Society and from the Danish Research Center for Lung Cancer; and reports that Medtronic has lent equipment to the Simulation Center at Odense University Hospital for a research project where she is the primary investigator.
Figures


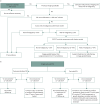
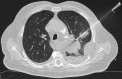
Similar articles
-
Innovations in thoracic imaging: CT, radiomics, AI and x-ray velocimetry.Respirology. 2022 Oct;27(10):818-833. doi: 10.1111/resp.14344. Epub 2022 Aug 14. Respirology. 2022. PMID: 35965430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A proposed methodology for detecting the malignant potential of pulmonary nodules in sarcoma using computed tomographic imaging and artificial intelligence-based models.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 21;13:1212526. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1212526. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37671060 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of lung cancer.Curr Probl Cancer. 2023 Apr;47(2):100966. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2023.100966. Epub 2023 Jun 4. Curr Probl Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37316337
-
The effect of direct referral for fast CT scan in early lung cancer detection in general practice. A clinical, cluster-randomised trial.Dan Med J. 2015 Mar;62(3):B5027. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25748876 Clinical Trial.
-
Prostate Cancer Radiogenomics-From Imaging to Molecular Characterization.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 15;22(18):9971. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189971. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576134 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Multimodal Imaging Techniques for Evaluating and Predicting the Efficacy of Immunotherapy for NSCLC.Cancer Manag Res. 2025 Jun 7;17:1073-1086. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S522136. eCollection 2025. Cancer Manag Res. 2025. PMID: 40503548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Holistic Approach to Implementing Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2025 Feb;16(1):257-278. doi: 10.1007/s13193-024-02079-6. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40114896 Review.
-
Absent preoperative non-small cell lung cancer confirmation and relevant stage migration in the era before neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy: implications for treatment decisions in resectable non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;14(5):1543-1557. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-2024-1120. Epub 2025 May 22. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40535091 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advancements in lung cancer research: a narrative review.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 31;14(3):975-990. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-979. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40248731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung Cancer-Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Treatment and Molecular Aspect (Review of Literature).Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 26;26(5):2049. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052049. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076671 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- De Wever W, Coolen J, Verschakelen JA. Imaging techniques in lung cancer. Breathe 2011; 7: 338–346. doi:10.1183/20734735.022110 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
