Syphilis Treatment: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Investigating Nonpenicillin Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 38595955
- PMCID: PMC11002953
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofae142
Syphilis Treatment: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Investigating Nonpenicillin Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
Background: Penicillin's long-standing role as the reference standard in syphilis treatment has led to global reliance. However, this dependence presents challenges, prompting the need for alternative strategies. We performed a systematic literature review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of these alternative treatments against nonneurological syphilis.
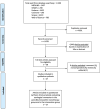
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, Embase, Cochrane, Scopus, and Web of Science from database inception to 28 August 2023, and we included studies that compared penicillin or amoxicillin monotherapy to other treatments for the management of nonneurological syphilis. Our primary outcome was serological cure rates. Random-effect models were used to obtain pooled mean differences, and heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 test.
Results: Of 6478 screened studies, 27 met the inclusion criteria, summing 6710 patients. The studies were considerably homogeneous, and stratified analyses considering each alternative treatment separately revealed that penicillin monotherapy did not outperform ceftriaxone (pooled odds ratio, 1.66 [95% confidence interval, .97-2.84]; I2 = 0%), azithromycin (0.92; [.73-1.18]; I2 = 0%), or doxycycline (0.82 [.61-1.10]; I2 = 1%) monotherapies with respect to serological conversion.
Conclusions: Alternative treatment strategies have serological cure rates equivalent to penicillin, potentially reducing global dependence on this antibiotic.
Keywords: efficacy comparison; nonneurological syphilis; penicillin; syphilis treatment; treatment alternatives.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Antibiotic treatment for newborns with congenital syphilis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 15;2(2):CD012071. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012071.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30776081 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic therapy for adults with neurosyphilis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 27;5(5):CD011399. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011399.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31132142 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Diagnostic Stewardship: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Blood Collection Diversion Devices Used to Reduce Blood Culture Contamination and Improve the Accuracy of Diagnosis in Clinical Settings.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023 Aug 11;10(9):ofad433. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofad433. eCollection 2023 Sep. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37674630 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Amoxicillin 3000 mg and Probenecid Versus 1500 mg Amoxicillin Monotherapy for Treating Syphilis in Patients With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: An Open-Label, Randomized, Controlled, Non-Inferiority Trial.Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Sep 11;77(5):779-787. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad278. Clin Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37157863 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Comment on Callado et al: "Syphilis Treatment: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Investigating Nonpenicillin Therapeutic Strategies".Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Jun 24;11(7):ofae324. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae324. eCollection 2024 Jul. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38957685 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Patients with Neurosyphilis in Emergency Department: A Retrospective Study of 12 Patients.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Oct 30;17:4773-4781. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S482264. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39494226 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding Horizons in Syphilis Treatment: Challenges, Advances, and Opportunities for Alternative Antibiotics.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025 Mar 13;22(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s11904-025-00725-4. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025. PMID: 40074945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and Treatment Outcomes of Syphilis among People with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Engaging in High-Risk Sexual Behavior: Real World Data from Northern Greece, 2019-2022.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 21;12(7):1256. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071256. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065024 Free PMC article.
-
The Obsolescence of Azithromycin for Syphilis Treatment and the Value of Contrasting Different Types of Evidence.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Jun 24;11(7):ofae325. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae325. eCollection 2024 Jul. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38957686 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Food and Drug Administration . FDA drug shortages, penicillin g benzathine injectable suspension. Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/drugshortages/dsp_ActiveIngredien.... Accessed 12 October 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

