Microplastics in the Amazon biome: State of the art and future priorities
- PMID: 38596029
- PMCID: PMC11002258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28851
Microplastics in the Amazon biome: State of the art and future priorities
Abstract
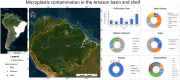
Microplastics (MPs) have been identified as a major potential threat to the biota and human health. Despite the exponential increase in MP research worldwide, few studies have focused on the extensive Amazon biome. To assess research priorities, the present study reviewed and summarized the available scientific knowledge on MPs in the Amazon, in addition to analyzing population and waste-management data, to evaluate potential sources of MPs in the hydrographic system. Poor sanitation conditions are a main source of MPs for the vast hydrographic basin, and, consequently, for the adjacent ocean. Secondary MPs predominated, mostly fibers (96% of debris), composed of polyamide (32%). Mean MP concentrations ranged from 0.34 to 38.3 particles.individual-1 in biota, 5 to 476,000 particles.m-3 in water, and 492.5 to 1.30848 × 107 particles.m-3 in sediment, values in close comparison with those found in areas profoundly affected by anthropogenic pollution. MPs were widespread in a range of Amazonian environments and species, and negative effects are probably occurring at various ecological levels. However, limited research, methodological constraints, flaws and the lack of standardization, combined with the continental dimensions of the Amazon, hampers the collection of the fundamental knowledge needed to reliably evaluate the impacts and implement effective mitigation measures. There is an urgent need to expand scientific data available for the region, improving local research infrastructure, and training and deploying local researchers.
Keywords: Plastic debris; Pollution; Review; SDG 14; South atlantic.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- GESAMP . In: Reports and Studies. Kershaw P.J., Turra A., Galgani F., editors. 2019. Guidelines for the monitoring and assessment of plastic litter and microplastics in the ocean. IMO/FAO/UNESCO-IOC/UNIDO/WMO/IAEA/UN/UNEP/UNDP/ISA Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection. GESAMP No. 99, 130 pp. ISSN: 1020–4873.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

