Tuberous sclerosis complex associated lymphangioleiomyomatosis caused by de novo mutation of TSC2 gene in Vietnam: A case report
- PMID: 38596252
- PMCID: PMC11002990
- DOI: 10.1002/rcr2.1346
Tuberous sclerosis complex associated lymphangioleiomyomatosis caused by de novo mutation of TSC2 gene in Vietnam: A case report
Abstract
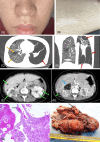
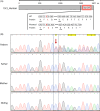
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) represents a rare, insidiously progressive disease of the pulmonary system, marked by cystic degradation of lung tissues leading to respiratory compromise. Pulmonary LAM has been identified as being associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) in its pulmonary manifestation (TSC-LAM), a multisystem genetic disorder resulting from mutations in either the TSC1 or TSC2 genes. Herein, we describe an early 20s female admitted to the hospital with dyspnea, chest pain, hypopigmented macules, and facial fibroadenomas. She has a medical history of renal angiomyolipomas (ALMs) and pneumothoraces. Diagnosis with LAM was confirmed through high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scan and histopathology of lung biopsy. Whole exome sequencing analysis identified a frameshift mutation c.4504del (p.L1502Cfs*74) in the patient's TSC2 gene. This variant was de novo due to its absence in the patient's parents. This is the first report on the clinical and genetic etiology of TSC-LAM in Vietnam.
Keywords: TSC2 gene; TSC‐LAM; pathogenic variants.
© 2024 The Authors. Respirology Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- McCarthy C, Gupta N, Johnson SR, Yu JJ, McCormack FX. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(11):1313–1327. - PubMed
-
- Cudzilo CJ, Szczesniak RD, Brody AS, Rattan MS, Krueger DA, Bissler JJ, et al. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis screening in women with tuberous sclerosis. Chest. 2013;144(2):578–585. - PubMed
-
- Li Y. TSC2: filling the GAP in the mTOR signaling pathway. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29(1):32–38. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

