Efflux pumps as potential targets for biofilm inhibition
- PMID: 38596384
- PMCID: PMC11002903
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1315238
Efflux pumps as potential targets for biofilm inhibition
Abstract
Biofilms account for a great deal of infectious diseases and contribute significantly to antimicrobial resistance. Efflux pumps confer antimicrobial resistance to microorganisms and involve multiple processes of biofilm formation. Efflux pump inhibitors (EPIs) are attracting considerable attention as a biofilm inhibition strategy. The regulatory functions of efflux pumps in biofilm formation such as mediating adherence, quorum sensing (QS) systems, and the expression of biofilm-associated genes have been increasingly identified. The versatile properties confer efflux pumps both positive and negative effects on biofilm formation. Furthermore, the expression and function of efflux pumps in biofilm formation are species-specific. Therefore, this review aims to detail the double-edged sword role of efflux pumps in biofilm formation to provide potential inhibition targets and give an overview of the effects of EPIs on biofilm formation.
Keywords: biofilm; efflux pump; efflux pump inhibitor; motility; quorum sensing.
Copyright © 2024 Ren, Wang, Zhou and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
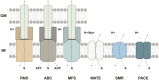
Figures

References
-
- Ahmadi F., Khalvati B., Eslami S., Mirzaii M., Roustaei N., Mazloomirad F., et al. . (2022). The inhibitory effect of Thioridazine on adeB efflux pump gene expression in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates using real time PCR. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 14, 132–136. doi: 10.18502/ajmb.v14i2.8884, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

