Evaluating Gabapentin Dosing, Efficacy and Safety in Infants
- PMID: 38596422
- PMCID: PMC11001217
- DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-29.2.159
Evaluating Gabapentin Dosing, Efficacy and Safety in Infants
Abstract
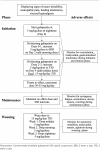
Objective: Gabapentin for management of neuropathic pain, irritability, neonatal abstinence syndrome, rescue sedation, feeding intolerance and visceral hyperalgesia in infants has grown over the past decade. There remains little guidance for indications, initiation, titration and maintenance dosing trends and assessment of outcomes. The primary objective was to describe gabapentin dosing, and the secondary objectives were to identify outcomes to assess efficacy and describe weaning practices.
Methods: A retrospective single-center study was performed in infants younger than 1 year who received gabapentin at Boston Children's Hospital between 2015 and 2021. The primary outcome was indication, initiation and maximum gabapentin dose. Secondary outcomes included mortality, adverse reactions and impact on feeding volumes, weight-for-age Z-scores and face, legs, activity, cry, consolability (FLACC) scores. Descriptive statistics were utilized.
Results: Sixty-six infants received gabapentin at a mean ± SD age of 5.5 ± 2.7 months (range of 0-11 months). The mean ± SD initiation dose of gabapentin was 8.6 ± 5.4 mg/kg/day with a median interval of 24 hours (8-24 hours). The maximum mean dose was 23.2 ± 14.4 mg/kg/day at a median interval of every 8 hours (8 hours). The most common indications for initiation were irritability, rescue sedation, and visceral hyperalgesia. There was a statistical improvement in weight-for-age Z scores from 24 hours prior to gabapentin initiation to 2 weeks after the maximum dose of gabapentin (-2.23 ± 1.78 to -1.66 ± 1.91, p < 0.001) and a reduction in FLACC scores (2.29 ± 1.64 to 1.52 ± 1.76, p = 0.007) from 24 hours prior to gabapentin initiation to 3 days after the maximum dose of gabapentin. Three patients experienced minor adverse events.
Conclusions: Gabapentin was well tolerated in infants. Initial gabapentin dosing of 5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours appears safe and consistent with other published studies in infants. The improvement in outcomes with few adverse events suggests a beneficial role for gabapentin.
Keywords: gabapentin; infants; irritability; neonates; pain; visceral hyperalgesia.
Copyright. Pediatric Pharmacy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, email: membership@pediatricpharmacy.org.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure. The authors declare no conflicts or financial interest in any product or service mentioned in the manuscript, including grants, equipment, medications, employment, gifts and honoraria. The authors had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Use of Gabapentin for Pain and Agitation in Neonates and Infants in a Neonatal ICU.J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2017 May-Jun;22(3):207-211. doi: 10.5863/1551-6776-22.3.207. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28638303 Free PMC article.
-
Gabapentin as add-on to morphine for severe neuropathic or mixed pain in children from age 3 months to 18 years - evaluation of the safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of a new gabapentin liquid formulation: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2019 Jan 15;20(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-3169-3. Trials. 2019. PMID: 30646965 Free PMC article.
-
Gabapentin for pain, movement disorders, and irritability in neonates and infants.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2020 Mar;62(3):386-389. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.14324. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31343730
-
Gabapentin dosing for neuropathic pain: evidence from randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials.Clin Ther. 2003 Jan;25(1):81-104. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(03)90011-7. Clin Ther. 2003. PMID: 12637113 Review.
-
Gabapentin dosing in the treatment of epilepsy.Clin Ther. 2003 May;25(5):1382-406. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(03)80127-3. Clin Ther. 2003. PMID: 12867216 Review.
Cited by
-
Visceral Pain in Preterm Infants with Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Underlying Mechanisms and Implications for Treatment.Paediatr Drugs. 2025 Mar;27(2):201-220. doi: 10.1007/s40272-024-00676-0. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Paediatr Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39752054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Gabapentin with a Focus on Topical Formulations to Treat Ocular Surface Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 11;17(5):623. doi: 10.3390/ph17050623. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correspondence on "Gabapentin for Delirium in Infants in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit".J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2025 Apr;30(2):298-301. doi: 10.5863/1551-6776-30.2.298. Epub 2025 Apr 14. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40717746 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics and Transfer of Gabapentin When Used as a Pain Adjunct for Cesarean Deliveries.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2025 Mar;14(3):551-560. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13295. Epub 2025 Jan 31. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39891423 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-2 agonists for refractory neurological symptoms in pediatric palliative care: a scoping review.Front Pediatr. 2025 May 14;13:1542482. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1542482. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40438778 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hauer JM, Wical BS, Charnas L. Gabapentin successfully manages chronic unexplained irritability in children with severe neurologic impairment. Pediatrics. 2007;119:e519–e522. - PubMed
-
- Hauer J, Mackey D. Treatment with gabapentin associated with resolution of apnea in two infants with neurologic impairment. J Palliat Med. 2013;16:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Burnsed JC, Heinan K, Letzkus L, Zanelli S. Gabapentin for pain, movement disorders, and irritability in neonates and infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2020;62(3):386–389. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous