Alkaline sphingomyelinase deficiency impairs intestinal mucosal barrier integrity and reduces antioxidant capacity in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis
- PMID: 38596488
- PMCID: PMC11000083
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1405
Alkaline sphingomyelinase deficiency impairs intestinal mucosal barrier integrity and reduces antioxidant capacity in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis
Abstract
Background: Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the colon with an unknown etiology. Alkaline sphingomyelinase (alk-SMase) is specifically expressed by intestinal epithelial cells, and has been reported to play an anti-inflammatory role. However, the underlying mechanism is still unclear.
Aim: To explore the mechanism of alk-SMase anti-inflammatory effects on intestinal barrier function and oxidative stress in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis.
Methods: Mice were administered 3% DSS drinking water, and disease activity index was determined to evaluate the status of colitis. Intestinal permeability was evaluated by gavage administration of fluorescein isothiocyanate dextran, and bacterial translocation was evaluated by measuring serum lipopolysaccharide. Intestinal epithelial cell ultrastructure was observed by electron microscopy. Western blotting and quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction were used to detect the expression of intestinal barrier proteins and mRNA, respectively. Serum oxidant and antioxidant marker levels were analyzed using commercial kits to assess oxidative stress levels.
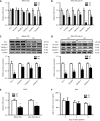
Results: Compared to wild-type (WT) mice, inflammation and intestinal permeability in alk-SMase knockout (KO) mice were more severe beginning 4 d after DSS induction. The mRNA and protein levels of intestinal barrier proteins, including zonula occludens-1, occludin, claudin-3, claudin-5, claudin-8, mucin 2, and secretory immunoglobulin A, were significantly reduced on 4 d after DSS treatment. Ultrastructural observations revealed progressive damage to the tight junctions of intestinal epithelial cells. Furthermore, by day 4, mitochondria appeared swollen and degenerated. Additionally, compared to WT mice, serum malondialdehyde levels in KO mice were higher, and the antioxidant capacity was significantly lower. The expression of the transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in the colonic mucosal tissue of KO mice was significantly decreased after DSS treatment. mRNA levels of Nrf2-regulated downstream antioxidant enzymes were also decreased. Finally, colitis in KO mice could be effectively relieved by the injection of tertiary butylhydroquinone, which is an Nrf2 activator.
Conclusion: Alk-SMase regulates the stability of the intestinal mucosal barrier and enhances antioxidant activity through the Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Keywords: Alkaline sphingomyelinase; Antioxidant capacity; Dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis; Intestinal mucosal barrier; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures



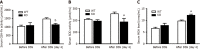
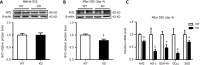

Similar articles
-
Effect of toll-like receptor 3 agonist poly I:C on intestinal mucosa and epithelial barrier function in mouse models of acute colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb 14;23(6):999-1009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.999. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28246473 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol ameliorates ulcerative colitis by upregulating Nrf2/HO‑1 pathway activity: Integrating animal experiments and network pharmacology.Mol Med Rep. 2024 May;29(5):77. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13201. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38488031
-
Effects of 17β-Estradiol on Colonic Permeability and Inflammation in an Azoxymethane/Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis Mouse Model.Gut Liver. 2018 Nov 15;12(6):682-693. doi: 10.5009/gnl18221. Gut Liver. 2018. PMID: 30400733 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effects of nutritional supplements on intestinal epithelial barrier functions in experimental colitis models in vivo.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug 14;25(30):4181-4198. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i30.4181. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31435172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling attenuates NFkappaB-inflammatory response and elicits apoptosis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Dec 1;76(11):1485-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.017. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18694732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Classical to Alternative Pathways of 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Synthesis: AlterAGs at the Crossroad of Endocannabinoid and Lysophospholipid Signaling.Molecules. 2024 Aug 4;29(15):3694. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153694. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

