Overview of the immunological mechanisms in hepatitis B virus reactivation: Implications for disease progression and management strategies
- PMID: 38596493
- PMCID: PMC11000084
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1295
Overview of the immunological mechanisms in hepatitis B virus reactivation: Implications for disease progression and management strategies
Abstract
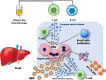
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation is a clinically significant challenge in disease management. This review explores the immunological mechanisms underlying HBV reactivation, emphasizing disease progression and management. It delves into host immune responses and reactivation's delicate balance, spanning innate and adaptive immunity. Viral factors' disruption of this balance, as are interactions between viral antigens, immune cells, cytokine networks, and immune checkpoint pathways, are examined. Notably, the roles of T cells, natural killer cells, and antigen-presenting cells are discussed, highlighting their influence on disease progression. HBV reactivation's impact on disease severity, hepatic flares, liver fibrosis progression, and hepatocellular carcinoma is detailed. Management strategies, including anti-viral and immunomodulatory approaches, are critically analyzed. The role of prophylactic anti-viral therapy during immunosuppressive treatments is explored alongside novel immunotherapeutic interventions to restore immune control and prevent reactivation. In conclusion, this comprehensive review furnishes a holistic view of the immunological mechanisms that propel HBV reactivation. With a dedicated focus on understanding its implications for disease progression and the prospects of efficient management strategies, this article contributes significantly to the knowledge base. The more profound insights into the intricate interactions between viral elements and the immune system will inform evidence-based approaches, ultimately enhancing disease management and elevating patient outcomes. The dynamic landscape of management strategies is critically scrutinized, spanning anti-viral and immunomodulatory approaches. The role of prophylactic anti-viral therapy in preventing reactivation during immunosuppressive treatments and the potential of innovative immunotherapeutic interventions to restore immune control and proactively deter reactivation.
Keywords: Disease progression; Hepatitis B virus reactivation; Immune response; Immunological mechanisms; Management strategies.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aliu TB, Majiyebo AJ, Tsado AN, Ibrahim HA, Berinyuy EB. Biology and molecular pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Biomed Natu and App Sci. 2022;2:28–36.
-
- Hsu YC, Huang DQ, Nguyen MH. Global burden of hepatitis B virus: current status, missed opportunities and a call for action. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;20:524–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

