Characterization of human respiratory syncytial virus in children with severe acute respiratory infection before and during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 38596821
- PMCID: PMC11002793
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2024.03.009
Characterization of human respiratory syncytial virus in children with severe acute respiratory infection before and during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Objectives: Annual outbreaks of human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) are caused by newly introduced and locally persistent strains. During the COVID-19 pandemic, global and local circulation of HRSV significantly decreased. This study was conducted to characterize HRSV in 2018-2022 and to analyze the impact of COVID-19 on the evolution of HRSV.
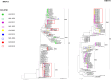
Design/methods: Combined oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal swabs were collected from children hospitalized with severe acute respiratory infection at two hospitals in Zambia. The second hypervariable region of the attachment gene G was targeted for phylogenetic analysis.
Results: Of 3113 specimens, 504 (16.2%) were positive for HRSV, of which 131 (26.0%) and 66 (13.1%) were identified as HRSVA and HRSVB, respectively. In early 2021, an increase in HRSV was detected, caused by multiple distinct clades of HRSVA and HRSVB. Some were newly introduced, whereas others resulted from local persistence.
Conclusions: This study provides insights into the evolution of HRSV, driven by global and local circulation. The COVID-19 pandemic had a temporal impact on the evolution pattern of HRSV. Understanding the evolution of HRSV is vital for developing strategies for its control.
Keywords: Molecular evolution; Respiratory syncytial virus; Severe acute respiratory infection; Zambia.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Rudan I, O'Brien KL, Nair H, Liu L, Theodoratou E, Qazi S, et al. Epidemiology and etiology of childhood pneumonia in 2010: estimates of incidence, severe morbidity, mortality, underlying risk factors and causative pathogens for 192 countries. J Glob Health. 2013;3 doi: 10.7189/jogh.03.010401. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Wang X, Blau DM, Caballero MT, Feikin DR, Gill CJ, et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2022;399:2047–2064. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00478-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

