Effects of silencing farnesyltransferase on the migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cells
- PMID: 38596954
- PMCID: PMC9396426
- DOI: 10.7518/hxkq.2022.04.004
Effects of silencing farnesyltransferase on the migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cells
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the effects of farnesyltransferase (FTase) on the migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of SACC-LM and SACC-83 cells in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma and determine the relative mechanism.
Methods: Three small interfering RNA (siRNA) sequences were designed and constructed based on the human FTase gene sequence. The SACC-LM and SACC-83 cells in the logarithmic growth period were used, and the expression of FTase was suppressed by liposomal transient transfection. The tested cells were categorized as the FTase-siRNA-1, FTase-siRNA-2, and FTase-siRNA-3 groups. Both negative control group (NC-siRNA) and blank control group (only transfection reagent was added) were set. The mRNA expression of FTase and HRAS was detected by quantitive real-time polymerase chain reaction, and the silencing efficiency was determined. The expression levels of FTase, HRAS, protein kinase B (AKT), phospho-AKT, p65, phospho-p65 (Ser563), E-cadherin, vimentin, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 protein, and HRAS membrane protein were detected by Western blot. Transwell assay and wound healing assay were used to detect the invasion and migration abilities of cells.
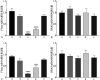
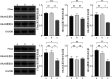
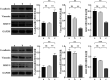
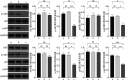
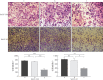
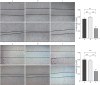
Results: The relative expression of FTase mRNA and protein in the FTase-siRNA-1 group decreased compared with those in the control group (P<0.05). HRAS mRNA and total protein expression had no significant difference (P>0.05), and the relative expression of HRAS membrane protein decreased (P<0.05). The relative expression of E-cadherin increased (P<0.05), vimentin decreased (P<0.05), and MMP-9 decreased (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the relative expression levels of the RAS/PI3K/AKT/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway-related proteins AKT and p65 (P>0.05), but the relative expression levels of phospho-AKT and phospho-p65 decreased. The invasion and migration ability of the FTase-siRNA-1 group significantly decreased compared with that in the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Silencing FTase in vitro could effectively inhibit the invasion and migration of SACC-LM and SACC-83 cells by interfering with the localization of the HRAS membrane protein and regulating the RAS/PI3K/AKT/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway to mediate EMT.
目的: 通过体外实验探讨法尼基转移酶(FTase)对涎腺腺样囊性癌SACC-LM和SACC-83细胞迁移侵袭及上皮间充质转化(EMT)的作用及其机制。方法: 针对人FTase基因序列设计构建3条小干扰RNA(si-RNA),采用处于对数生长期的SACC-LM及SACC-83细胞,经脂质体瞬时转染技术抑制细胞FTase表达,分别命名为FTase-siRNA-1组、FTase-siRNA-2组、FTase-siRNA-3组,同时设置阴性对照组(NC-siRNA),空白对照组(仅加入转染试剂)。采用实时荧光定量逆转录聚合酶链反应检测FTase、HRAS的mRNA表达,选择沉默效率最高的FTase-siRNA进行后续实验;蛋白质免疫印迹法检测FTase、HRAS、蛋白激酶B(AKT)、磷酸化AKT、p65、磷酸化p65(Ser563)、上皮钙依赖黏附蛋白、波形蛋白、基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP-9)的蛋白表达以及HRAS膜蛋白表达;Transwell小室及细胞划痕实验检测细胞的侵袭和迁移能力。结果: 与空白对照组及阴性对照组相比,FTase-siRNA-1组mRNA及蛋白相对表达量均降低(P<0.05),HRAS mRNA和总蛋白表达的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),HRAS膜蛋白相对表达量降低(P<0.05),上皮钙依赖黏附蛋白相对表达量升高(P<0.05),波形蛋白相对表达量降低(P<0.05),MMP-9蛋白相对表达量降低(P<0.05),RAS/PI3K/AKT/核因子-κB信号通路相关蛋白AKT、p65相对表达量的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),但磷酸化AKT、磷酸化p65蛋白相对表达量降低;与空白及阴性对照组相比,FTase-siRNA-1组细胞侵袭及迁移能力显著下降(P<0.05)。结论: 体外沉默FTase可有效抑制人涎腺腺样囊性癌细胞SACC-LM和SACC-83的侵袭、迁移能力,其作用可能是通过干扰HRAS膜蛋白的定位,调控RAS/PI3K/AKT/核因子-κB信号通路,介导EMT而实现。.
Keywords: HRAS; farnesyltransferase; invasion; migration; salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突声明:作者声明本文无利益冲突。
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of silencing Ras homolog family member C on proliferation, invasion, and migration of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Dec 1;42(6):723-734. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2024.2024092. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39610069 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
[Effects of farnesyltransferase silencing on the migration and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Apr 1;38(2):177-184. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2020.02.012. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32314892 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
BTBD7 silencing inhibited epithelial- mesenchymal transition (EMT) via regulating Slug expression in human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2017 Dec 6;20(4):461-468. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170262. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 28946551
-
BRD4 inhibition suppresses cell growth, migration and invasion of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma.Biol Res. 2017 May 25;50(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s40659-017-0124-9. Biol Res. 2017. PMID: 28545522 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of miR-202-5p silencing PIK3CA gene expression on proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer SiHa cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway activation.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Nov;476(11):4031-4044. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04211-4. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34244973
References
-
- Lee AN, Givi B, Osborn VW, et al. Patterns of care and survival of adjuvant radiation for major salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma[J] Laryngoscope. 2017;127(9):2057–2062. - PubMed
-
- Hodge RG, Schaefer A, Howard SV, et al. RAS and RHO family GTPase mutations in cancer: twin sons of different mothers[J] Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2020;55(4):386–407. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
