Bone erosions and joint damage caused by chikungunya virus: a systematic review
- PMID: 38597523
- PMCID: PMC11000508
- DOI: 10.1590/0037-8682-0433-2023
Bone erosions and joint damage caused by chikungunya virus: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Chikungunya fever is an emerging global infection transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes that manifests as an acute febrile illness with joint pain and can lead to chronic arthritis. The mechanism underlying chronic joint damage remains unclear; however, chronic chikungunya arthritis shares similarities with rheumatoid arthritis. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs have revolutionized rheumatoid arthritis treatment by preventing joint damage. However, the role of these therapies in chronic chikungunya arthritis has not been determined. We conducted a systematic review to evaluate the burden of joint structural damage in chronic chikungunya arthritis to help to define the role of disease-modifying therapy in this disease.
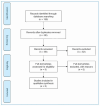
Methods: This systematic review included retrospective and prospective studies, trials, and case reports evaluating joint damage caused by chikungunya virus. Various databases were searched without any date or language restrictions. Study selection was conducted independently by two researchers, and data were extracted from the articles selected.
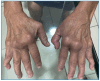
Results: A total of 108 studies were initially evaluated, with 8 meeting the inclusion criteria. Longitudinal studies have reported persistent joint pain from chikungunya infection and the progression of radiographic joint damage up to 13 years post-infection. Joint imaging revealed synovial inflammation, bone erosion, and cartilage destruction in patients with chronic chikungunya arthritis.
Conclusions: Few studies have addressed chikungunya-induced joint damage, limiting our understanding of chronic chikungunya arthritis. Nevertheless, chronic chikungunya arthritis has similarities to rheumatoid arthritis. The success of early disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy in rheumatoid arthritis underscores the need for comprehensive research on its role in chikungunya arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rodríguez-Morales AJ, Cardona-Ospina JA, Fernanda Urbano-Garzón S, Sebastian Hurtado-Zapata J. Arthritis Care Res. 12. Vol. 68. Hoboken: 2016. Prevalence of Post-Chikungunya Infection Chronic Inflammatory Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis; pp. 1849–1858. - PubMed
-
- Kril V, Aïqui-Reboul-Paviet O, Briant L, Amara A. New Insights into Chikungunya Virus Infection and Pathogenesis. Annu Rev Virol. 2021;8(1):327–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical