Somatic and intergenerational G4C2 hexanucleotide repeat instability in a human C9orf72 knock-in mouse model
- PMID: 38597682
- PMCID: PMC11162798
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae250
Somatic and intergenerational G4C2 hexanucleotide repeat instability in a human C9orf72 knock-in mouse model
Abstract
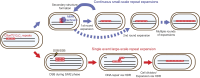
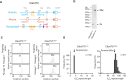
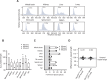
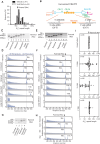
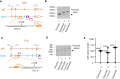
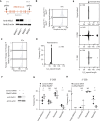
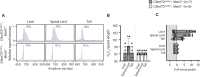
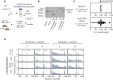
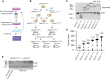
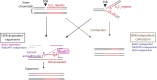
Expansion of a G4C2 repeat in the C9orf72 gene is associated with familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD). To investigate the underlying mechanisms of repeat instability, which occurs both somatically and intergenerationally, we created a novel mouse model of familial ALS/FTD that harbors 96 copies of G4C2 repeats at a humanized C9orf72 locus. In mouse embryonic stem cells, we observed two modes of repeat expansion. First, we noted minor increases in repeat length per expansion event, which was dependent on a mismatch repair pathway protein Msh2. Second, we found major increases in repeat length per event when a DNA double- or single-strand break (DSB/SSB) was artificially introduced proximal to the repeats, and which was dependent on the homology-directed repair (HDR) pathway. In mice, the first mode primarily drove somatic repeat expansion. Major changes in repeat length, including expansion, were observed when SSB was introduced in one-cell embryos, or intergenerationally without DSB/SSB introduction if G4C2 repeats exceeded 400 copies, although spontaneous HDR-mediated expansion has yet to be identified. These findings provide a novel strategy to model repeat expansion in a non-human genome and offer insights into the mechanism behind C9orf72 G4C2 repeat instability.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Lander E.S., Linton L.M., Birren B., Nusbaum C., Zody M.C., Baldwin J., Devon K., Dewar K., Doyle M., FitzHugh W. et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001; 409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Dion V. Tissue specificity in DNA repair: lessons from trinucleotide repeat instability. Trends Genet. 2014; 30:220–229. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

