Technical note: Visual, rapid, scintillation point dosimetry for in vivo MV photon beam radiotherapy treatments
- PMID: 38598093
- PMCID: PMC11321933
- DOI: 10.1002/mp.17071
Technical note: Visual, rapid, scintillation point dosimetry for in vivo MV photon beam radiotherapy treatments
Abstract
Background: While careful planning and pre-treatment checks are performed to ensure patient safety during external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), inevitable daily variations mean that in vivo dosimetry (IVD) is the only way to attain the true delivered dose. Several countries outside the US require daily IVD for quality assurance. However, elsewhere, the manual labor and time considerations of traditional in vivo dosimeters may be preventing frequent use of IVD in the clinic.
Purpose: This study expands upon previous research using plastic scintillator discs for optical dosimetry for electron therapy treatments. We present the characterization of scintillator discs for in vivo x-ray dosimetry and describe additional considerations due to geometric complexities.
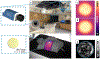
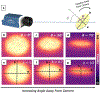
Methods: Plastic scintillator discs were coated with reflective white paint on all sides but the front surface. An anti-reflective, matte coating was applied to the transparent face to minimize specular reflection. A time-gated iCMOS camera imaged the discs under various irradiation conditions. In post-processing, background-subtracted images of the scintillators were fit with Gaussian-convolved ellipses to extract several parameters, including integral output, and observation angle.
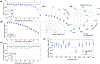
Results: Dose linearity and x-ray energy independence were observed, consistent with ideal characteristics for a dosimeter. Dose measurements exhibited less than 5% variation for incident beam angles between 0° and 75° at the anterior surface and 0-60 at the posterior surface for exit beam dosimetry. Varying the angle between the disc surface and the camera lens did not impact the integral output for the same dose up to 55°. Past this point, up to 75°, there is a sharp falloff in response; however, a correction can be used based on the detected width of the disc. The reproducibility of the integral output for a single disc is 2%, and combined with variations from the gantry angle, we report the accuracy of the proposed scintillator disc dosimeters as ±5.4%.
Conclusions: Plastic scintillator discs have characteristics that are well-suited for in vivo optical dosimetry for x-ray radiotherapy treatments. Unlike typical point dosimeters, there is no inherent readout time delay, and an optical recording of the measurement is saved after treatment for future reference. While several factors influence the integral output for the same dose, they have been quantified here and may be corrected in post-processing.
Keywords: in vivo dosimetry; photon therapy; scintillation imaging.
© 2024 American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors S.M.D., P.B., L.A.J., and B.W.P are affiliated with DoseOptics, LLC, who provided hardware support for this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Design and characterization of a novel scintillator array for UHDR PBS proton therapy surface dosimetry.Med Phys. 2025 Jul;52(7):e17922. doi: 10.1002/mp.17922. Epub 2025 May 31. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40450336 Free PMC article.
-
Cerenkov free micro-dosimetry in small-field radiation therapy technique.Phys Med Biol. 2024 Jun 12;69(12). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ad51c6. Phys Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38810619
-
Characterization of a practically designed plastic scintillation plate dosimeter.Med Phys. 2025 Jul;52(7):e17904. doi: 10.1002/mp.17904. Epub 2025 May 31. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40450380 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of the precision and accuracy of dose measurements in photon radiotherapy using polymer and Fricke MRI gel dosimetry.Phys Med Biol. 2002 Oct 21;47(20):R107-21. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/47/20/201. Phys Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12433119
Cited by
-
Cherenkov imaging combined with scintillation dosimetry provides real-time positional and dose monitoring for radiotherapy patients with cardiac implanted electronic devices.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024 Sep 12;32:100642. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2024.100642. eCollection 2024 Oct. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39315342 Free PMC article.
-
Design and characterization of a novel scintillator array for UHDR PBS proton therapy surface dosimetry.Med Phys. 2025 Jul;52(7):e17922. doi: 10.1002/mp.17922. Epub 2025 May 31. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40450336 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging system for real-time, full-field pulse-by-pulse surface dosimetry of UHDR electron beams.Med Phys. 2025 Jun;52(6):5026-5031. doi: 10.1002/mp.17784. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40170414
-
Robust Real-time Segmentation of Bio-Morphological Features in Human Cherenkov Imaging during Radiotherapy via Deep Learning.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 9:arXiv:2409.05666v1. ArXiv. 2024. Update in: Med Phys. 2025 Aug;52(8):e18002. doi: 10.1002/mp.18002. PMID: 39314506 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Visual Dose Monitoring for Whole Breast Radiation Therapy Treatments via Combined Cherenkov Imaging and Scintillation Dosimetry.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2025 Feb 1;121(2):365-374. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.08.033. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2025. PMID: 39182736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan MF, Witztum A, Valdes G. Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Radiotherapy QA. Front Artif Intell. 2020;3. Accessed September 1, 2023. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frai.2020.577620 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

