Axonal protection by combination of ripasudil and brimonidine with upregulation of p-AMPK in TNF-induced optic nerve degeneration
- PMID: 38598101
- PMCID: PMC11006787
- DOI: 10.1007/s10792-024-03095-9
Axonal protection by combination of ripasudil and brimonidine with upregulation of p-AMPK in TNF-induced optic nerve degeneration
Abstract
Purpose: The ROCK inhibitor ripasudil hydrochloride hydrate was shown to have axonal protective effects in TNF-induced optic nerve degeneration. The α2-adrenoreceptor agonist brimonidine was also shown to exert axonal protection. The current study aimed to elucidate whether additive axonal protection was achieved by the simultaneous injection of ripasudil and brimonidine and examine the association with AMPK activation.
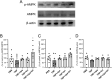
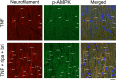
Methods: Intravitreal administration was performed in the following groups: PBS, TNF, or TNF with ripasudil, with brimonidine, or with a combination of ripasudil and brimonidine. Axon numbers were counted to evaluate the effects against axon loss. Immunoblot analysis was performed to examine phosphorylated AMPK expression in optic nerves, and immunohistochemical analysis was performed to evaluate the expression levels of p-AMPK and neurofilament in the optic nerve.
Results: Both ripasudil alone or brimonidine alone resulted in significant neuroprotection against TNF-induced axon loss. The combination of ripasudil and brimonidine showed additive protective effects. Combined ripasudil and brimonidine plus TNF significantly upregulated p-AMPK levels in the optic nerve compared with the TNF groups. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that p-AMPK is present in axons and enhanced by combination therapy.
Conclusion: The combination of ripasudil and brimonidine may have additive protective effects compared with single-agent treatment alone. These protective effects may be at least partially associated with AMPK activation.
Keywords: AMPK; Brimonidine; Glaucoma; Ripasudi.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Inoue T, Tanihara H (2013) Rho-associated kinase inhibitors: a novel glaucoma therapy. Prog Retin Eye Res 37:1–12. 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.05.002 - PubMed
-
- Sit AJ, Gupta D, Kazemi A, McKee H, Challa P, Liu KC, Lopez J, Kopczynski C, Heah T (2021) Netarsudil improves trabecular outflow facility in patients with primary open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension: a phase 2 study. Am J Ophthalmol 226:262–269. 10.1016/j.ajo.2021.01.019 - PubMed
-
- Vidal-Sanz M, Lafuente MP, Mayor S, Imperial JMD, Villegas-Pérez MP (2001) Retinal ganglion cell death induced by retinal ischemia. Neuroprotective effects of two alpha-2 agonists. Surv Ophthalmol 45:S261–S267 - PubMed
-
- Kim HS, Chang YI, Kim JH, Park CK (2007) Alteration of retinal intrinsic survival signal and effect of alpha2-adrenergic receptor agonist in the retina of the chronic ocular hypertension rat. Vis Neurosci 24:127–139. 10.1017/S0952523807070150 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

