The transcription factor BMI1 increases hypoxic signaling in oral cavity epithelia
- PMID: 38599260
- PMCID: PMC11370312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167161
The transcription factor BMI1 increases hypoxic signaling in oral cavity epithelia
Abstract
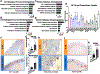
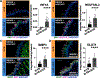
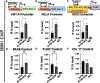
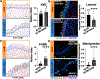
The tongue epithelium is maintained by a proliferative basal layer. This layer contains long-lived stem cells (SCs), which produce progeny cells that move up to the surface as they differentiate. B-lymphoma Mo-MLV insertion region 1 (BMI1), a protein in mammalian Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 (PRC1) and a biomarker of oral squamous cell carcinoma, is expressed in almost all basal epithelial SCs of the tongue, and single, Bmi1-labelled SCs give rise to cells in all epithelial layers. We previously developed a transgenic mouse model (KrTB) containing a doxycycline- (dox) controlled, Tet-responsive element system to selectively overexpress Bmi1 in the tongue basal epithelial SCs. Here, we used this model to assess BMI1 actions in tongue epithelia. Genome-wide transcriptomics revealed increased levels of transcripts involved in the cellular response to hypoxia in Bmi1-overexpressing (KrTB+DOX) oral epithelia even though these mice were not subjected to hypoxia conditions. Ectopic Bmi1 expression in tongue epithelia increased the levels of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF1α) and HIF1α targets linked to metabolic reprogramming during hypoxia. We used chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to demonstrate that Bmi1 associates with the promoters of HIF1A and HIF1A-activator RELA (p65) in tongue epithelia. We also detected increased SC proliferation and oxidative stress in Bmi1-overexpressing tongue epithelia. Finally, using a human oral keratinocyte line (OKF6-TERT1R), we showed that ectopic BMI1 overexpression decreases the oxygen consumption rate while increasing the extracellular acidification rate, indicative of elevated glycolysis. Thus, our data demonstrate that high BMI1 expression drives hypoxic signaling, including metabolic reprogramming, in normal oral cavity epithelia.
Keywords: Epigenetics; HIF1α; Metabolic reprogramming; Oral epithelial stem cells; Transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Allegra E, Trapasso S, Pisani D, and Puzzo L. (2014). The role of BMI1 as a biomarker of cancer stem cells in head and neck cancer: a review. Oncology 86, 199–205. - PubMed
-
- Bandookwala M, and Sengupta P. (2020). 3-Nitrotyrosine: a versatile oxidative stress biomarker for major neurodegenerative diseases. The International journal of neuroscience 130, 1047–1062. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee Mustafi S, Aznar N, Dwivedi SK, Chakraborty PK, Basak R, Mukherjee P, Ghosh P, and Bhattacharya R. (2016). Mitochondrial BMI1 maintains bioenergetic homeostasis in cells. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 30, 4042–4055. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

