FGF21 ameliorates septic liver injury by restraining proinflammatory macrophages activation through the autophagy/HIF-1α axis
- PMID: 38599281
- PMCID: PMC11954821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.004
FGF21 ameliorates septic liver injury by restraining proinflammatory macrophages activation through the autophagy/HIF-1α axis
Abstract
Introduction: Sepsis, a systemic immune syndrome caused by severe trauma or infection, poses a substantial threat to the health of patients worldwide. The progression of sepsis is heavily influenced by septic liver injury, which is triggered by infection and cytokine storms, and has a significant impact on the tolerance and prognosis of septic patients. The objective of our study is to elucidate the biological role and molecular mechanism of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) in the process of sepsis.
Objectives: This study was undertaken in an attempt to elucidate the function and molecular mechanism of FGF21 in therapy of sepsis.
Methods: Serum concentrations of FGF21 were measured in sepsis patients and septic mice. Liver injury was compared between mice FGF21 knockout (KO) mice and wildtype (WT) mice. To assess the therapeutic potential, recombinant human FGF21 was administered to septic mice. Furthermore, the molecular mechanism of FGF21 was investigated in mice with myeloid-cell specific HIF-1α overexpression mice (LyzM-CreDIO-HIF-1α) and myeloid-cell specific Atg7 knockout mice (Atg7△mye).
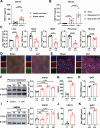
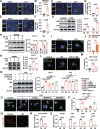
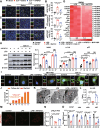
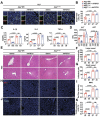
Results: Serum level of FGF21 was significantly increased in sepsis patients and septic mice. Through the use of recombinant human FGF21 (rhFGF21) and FGF21 KO mice, we found that FGF21 mitigated septic liver injury by inhibiting the initiation and propagation of inflammation. Treatment with rhFGF21 effectively suppressed the activation of proinflammatory macrophages by promoting macroautophagy/autophagy degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). Importantly, the therapeutic effect of rhFGF21 against septic liver injury was nullified in LyzM-CreDIO-HIF-1α mice and Atg7△mye mice.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that FGF21 considerably suppresses inflammation upon septic liver injury through the autophagy/ HIF-1α axis.
Keywords: Autophagy; FGF21; HIF-1α; Liver injury; Macrophage; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Araloside A alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via PHD2/HIF-1α in macrophages.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:156089. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156089. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39366158
-
Cynaroside prevents macrophage polarization into pro-inflammatory phenotype and alleviates cecal ligation and puncture-induced liver injury by targeting PKM2/HIF-1α axis.Fitoterapia. 2021 Jul;152:104922. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2021.104922. Epub 2021 May 11. Fitoterapia. 2021. PMID: 33984439
-
Norisoboldine Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Modulating Macrophage Polarization via PKM2/HIF-1α/PGC-1α Pathway.Biol Pharm Bull. 2021;44(10):1536-1547. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b21-00457. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 34602563
-
rTM reprograms macrophages via the HIF-1α/METTL3/PFKM axis to protect mice against sepsis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Nov 16;81(1):456. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05489-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39549085 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of FGF21 and its role in cardiac hypertrophy.J Adv Res. 2025 Mar 13:S2090-1232(25)00148-1. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2025.03.007. Online ahead of print. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 40089060 Review.
Cited by
-
FGF21, a modulator of astrocyte reactivity, protects against ischemic brain injury through anti-inflammatory and neurotrophic pathways.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Jul;46(7):1834-1851. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01462-x. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40021824 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin Attenuates Liver Fibrosis via Autophagy Induction.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jul;29(13):e70696. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70696. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40611443 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Sep 3;20(1):20251231. doi: 10.1515/med-2025-1231. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40918153 Free PMC article.
-
The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Formononetin, an Active Constituent of Pueraria montana Var. Lobata, via Modulation of Macrophage Autophagy and Polarization.Molecules. 2025 Jan 6;30(1):196. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010196. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39795251 Free PMC article.
-
Cell death signaling and immune regulation: new perspectives on targeted therapy for sepsis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Aug 15;30(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00784-w. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40817040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li A., Ling L., Qin H., et al. Epidemiology, Management, and outcomes of sepsis in intensive Care units among countries of differing National Wealth across Asia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 - PubMed
-
- Strnad P., Tacke F., Koch A., Trautwein C. Liver - guardian, modifier and target of sepsis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14(1):55–66. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

