PsiOvi Staging Model for Schizophrenia (PsiOvi SMS): A New Internet Tool for Staging Patients with Schizophrenia
- PMID: 38599765
- PMCID: PMC11059252
- DOI: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2024.17
PsiOvi Staging Model for Schizophrenia (PsiOvi SMS): A New Internet Tool for Staging Patients with Schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: One of the challenges of psychiatry is the staging of patients, especially those with severe mental disorders. Therefore, we aim to develop an empirical staging model for schizophrenia.
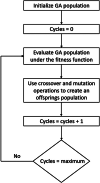
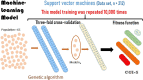
Methods: Data were obtained from 212 stable outpatients with schizophrenia: demographic, clinical, psychometric (PANSS, CAINS, CDSS, OSQ, CGI-S, PSP, MATRICS), inflammatory peripheral blood markers (C-reactive protein, interleukins-1RA and 6, and platelet/lymphocyte [PLR], neutrophil/lymphocyte [NLR], and monocyte/lymphocyte [MLR] ratios). We used machine learning techniques to develop the model (genetic algorithms, support vector machines) and applied a fitness function to measure the model's accuracy (% agreement between patient classification of our model and the CGI-S).
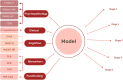
Results: Our model includes 12 variables from 5 dimensions: 1) psychopathology: positive, negative, depressive, general psychopathology symptoms; 2) clinical features: number of hospitalizations; 3) cognition: processing speed, visual learning, social cognition; 4) biomarkers: PLR, NLR, MLR; and 5) functioning: PSP total score. Accuracy was 62% (SD = 5.3), and sensitivity values were appropriate for mild, moderate, and marked severity (from 0.62106 to 0.6728).
Discussion: We present a multidimensional, accessible, and easy-to-apply model that goes beyond simply categorizing patients according to CGI-S score. It provides clinicians with a multifaceted patient profile that facilitates the design of personalized intervention plans.
Keywords: clinical tool; empirical staging model; multidimensional model; personalized intervention; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to the submitted work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

