Messenger RNA transport on lysosomal vesicles maintains axonal mitochondrial homeostasis and prevents axonal degeneration
- PMID: 38600167
- PMCID: PMC11156585
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01619-1
Messenger RNA transport on lysosomal vesicles maintains axonal mitochondrial homeostasis and prevents axonal degeneration
Abstract
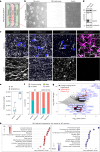
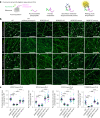
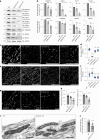
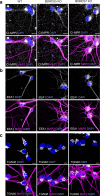
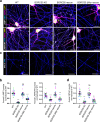
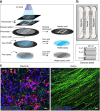
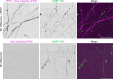
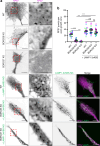
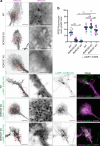
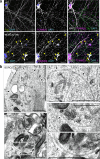
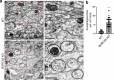
In neurons, RNA granules are transported along the axon for local translation away from the soma. Recent studies indicate that some of this transport involves hitchhiking of RNA granules on lysosome-related vesicles. In the present study, we leveraged the ability to prevent transport of these vesicles into the axon by knockout of the lysosome-kinesin adaptor BLOC-one-related complex (BORC) to identify a subset of axonal mRNAs that depend on lysosome-related vesicles for transport. We found that BORC knockout causes depletion of a large group of axonal mRNAs mainly encoding ribosomal and mitochondrial/oxidative phosphorylation proteins. This depletion results in mitochondrial defects and eventually leads to axonal degeneration in human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived and mouse neurons. Pathway analyses of the depleted mRNAs revealed a mechanistic connection of BORC deficiency with common neurodegenerative disorders. These results demonstrate that mRNA transport on lysosome-related vesicles is critical for the maintenance of axonal homeostasis and that its failure causes axonal degeneration.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Ballabio A, Bonifacino JS. Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21:101–118. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FI2 GM142475/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- ZIC HD008986/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- NIGMS FI2GM142475/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- ZIA HD001607/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 HD001607/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

